Filter
1109
Text search:
mali
Featured
75
254
Language
Document type
547
295
82
57
45
21
19
13
11
8
6
4
Countries / Regions
163
152
147
131
100
91
85
83
73
62
61
58
50
49
40
39
39
28
23
20
20
18
18
17
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
12
11
11
11
11
11
9
9
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
313
92
77
62
59
15
6
Toolboxes
199
80
59
53
48
47
37
35
33
32
28
27
21
17
15
12
11
9
9
8
7
6
4
2
2
1
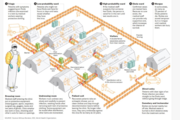
Please go to the the website http://www.msf.org.uk/ebola#Ebola%20centre and hover over the image for an interactive guide to Ebola
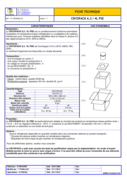
Le Cryopack 6.2/4L PSE est un conditionnement isotherme permettant l’expédition en température basse (réfrigération ou congélation) de matières infectieuses pour l’homme (matières identifiées dans la classe 6, division 6.2 des réglementations IATA, ADR et IMDG).
Please open the course from the website http://www.wiredhealthresources.net/mod-ebola.html