Filter
6662
Text search:
health
risks
Featured
638
1552
Language
6436
208
177
143
116
63
56
30
12
11
10
8
7
6
6
6
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Document type
3117
1305
970
424
320
213
123
72
32
30
28
11
6
5
1
Countries / Regions
430
183
172
141
129
117
115
111
110
103
100
98
95
93
90
87
77
77
71
64
63
61
60
58
45
45
44
44
40
37
37
35
32
31
31
31
31
30
30
30
29
29
28
26
26
24
23
22
21
19
18
18
17
17
16
15
14
13
13
13
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
8
8
7
7
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
978
283
269
187
186
140
99
77
74
70
48
47
43
38
37
35
34
34
30
30
29
29
28
28
28
27
27
26
26
25
24
24
23
20
20
19
19
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
17
17
16
16
16
16
16
15
15
15
15
15
15
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Publication Years
1
2459
3671
506
22
2
1
Category
2081
535
460
427
392
165
47
Toolboxes
726
544
411
342
262
254
240
230
188
172
168
157
156
138
129
114
111
102
90
85
67
58
49
46
17
8
2
The risks of the use of nuclear, radiological, biological or chemical (NRBC) weapons are heterogeneous. Each risk has its own implications for developing and deploying any capacity to assist victims of an NRBC event and, in parallel, for the
...
health and security of the people bringing this assistance. At an international level, there are no plans for assisting the victims of an NRBC event which are both adequate and safe. Recognizing
the realities of the contexts associated with each risk throws up numerous challenges; such recognition is also a prerequisite for addressing these challenges. The realities that have to be considered relate to:
1. developing, acquiring, training for and planning an NRBC response capacity;
2. deploying a response capacity in an NRBC event;
3. the mandates and policies of international organizations pertaining to NRBC events. The challenges that will pose the greatest difficulty for a humanitarian organization are those for which the solutions are ‘non-buyable’ and which involve making extremely difficult decisions. Attempting to assist victims of an NRBC event without a reality-based approach might generate ineffective and unacceptably dangerous situations for those involved.
more
The document emphasizes integrating environmental considerations into nutrition programs. It introduces a screening tool piloted across ten projects to identify environmental risks and opportunities, fostering sustainable practices in food systems.
...
The tool promotes collaboration, co-learning, and actionable steps to align nutrition goals with environmental sustainability, ensuring long-term benefits for health and ecosystems.
more
Not all that bleeds is Ebola
recommended
How has the DRC Ebola outbreak impacted Sexual and Reproductive Health in North-Kivu?
Recommendations (more specifics found in the assessment):
1. Sexual and reproductive health needs and services
...
are to be embedded in the EVD response from the outset.
2. Reduce delays at every stage of the patient journey, particularly for women experiencing obstetric complications, including complications from abortion.
3. Support individuals and communities to mitigate SRH risks posed during and after EVD epidemic:
4. Formulate SRH guidelines for the EVD context involving experts in all relevant fields.
more
Focusing on preventing and mitigating COVID-19 related risks, the standards aim to protect the health and safety of personnel, while ensuring that organizations continue to deliver on their mandates
...
. Attention is paid to non-discrimination and ensuring that all personnel, regardless of nationality or contractual type is equally covered and protected by the minimum standards in the COVID-19 context. It is acknowledged that the implementation of such standards may entail additional costs for organizations, for which a dialogue with donors may be warranted.
more
The ECDC webpage on malaria provides an overview of the disease, emphasizing that while malaria is mostly travel-related in the EU/EEA, it remains a serious global health threat. It outlines symptoms, affected populations, travel-associated
...
risks, and highlights the importance of prevention, surveillance, and data monitoring.
more
Long-term exposure of humans to air pollution enhances the risk of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. A novel Global Exposure Mortality Model (GEMM) has been derived from many cohort studies, providing much-improved coverage of the exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5). We applied the GE
...
MM to assess excess mortality attributable to ambient air pollution on a global scale and compare to other risk factors.
Methods and results
We used a data-informed atmospheric model to calculate worldwide exposure to PM2.5 and ozone pollution, which was combined with the GEMM to estimate disease-specific excess mortality and loss of life expectancy (LLE) in 2015. Using this model, we investigated the effects of different pollution sources, distinguishing between natural (wildfires, aeolian dust) and anthropogenic emissions, including fossil fuel use. Global excess mortality from all ambient air pollution is estimated at 8.8 (7.11–10.41) million/year, with an LLE of 2.9 (2.3–3.5) years, being a factor of two higher than earlier estimates, and exceeding that of tobacco smoking. The global mean mortality rate of about 120 per 100 000 people/year is much exceeded in East Asia (196 per 100 000/year) and Europe (133 per 100 000/year). Without fossil fuel emissions, the global mean life expectancy would increase by 1.1 (0.9–1.2) years and 1.7 (1.4–2.0) years by removing all potentially controllable anthropogenic emissions. Because aeolian dust and wildfire emission control is impracticable, significant LLE is unavoidable.
Conclusion
Ambient air pollution is one of the main global health risks, causing significant excess mortality and LLE, especially through cardiovascular diseases. It causes an LLE that rivals that of tobacco smoking. The global mean LLE from air pollution strongly exceeds that by violence (all forms together), i.e. by an order of magnitude (LLE being 2.9 and 0.3 years, respectively).
more
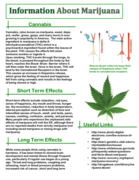
The pamphlet "Marijuana" explains the effects and risks of cannabis use. It describes THC, the psychoactive compound in cannabis, which binds to cannabinoid receptors in the brain, causing effects like relaxation, altered perception, and euphoria. S
...
hort-term effects include red eyes, hunger, and anxiety, while long-term effects may involve memory loss, lung problems, and slowed brain development, especially with early and frequent use. It highlights the potential for negative impacts on mental and physical health while noting there are no direct deaths solely from marijuana use. The pamphlet provides links to resources for further information and recovery options.
more
The framework responds to the demand from Member States and partners for guidance on how the health sector and its operational basis in health systems can systematically and effectively address the
...
challenges increasingly presented by climate variability and change. This framework has been designed in light of the increasing evidence of climate change and its associated health risks (1); global, regional and national policy mandates to protect population health (2); and a rapidly emerging body of practical experience in building health resilience to climate change (3).
more
Event-based surveillance (EBS) is defined as the organized collection, monitoring, assessment and interpretation of mainly unstructured ad hoc information regarding health events or risks, which may
...
represent an acute risk to health. Both indicator-based and event-based surveillance components serve the early warning and response (EWAR) function of the public health surveillance system. The Framework for Event-based Surveillance offers guidance to public health practitioners seeking to implement EBS at each administrative level in healthier countries.
more
A Diabetes Awareness Poster is used to raise awareness about diabetes and its related health issues. It is typically used in public places such as hospitals, clinics, and community centers to inform people about the
...
risks, symptoms, and management of diabetes.
more
The CDC report on Preventing Diarrheal Disease in Developing Countries highlights five effective household water treatment methods to reduce waterborne illnesses, which cause millions of deaths annually. These methods include ceramic filtration, solar disinfection (SODIS), flocculant/disinfectant po
...
wder (PUR), household chlorination, and slow sand filtration. Each method varies in effectiveness, cost, and ease of use, with benefits such as pathogen removal, affordability, and scalability, but also challenges like maintenance, recontamination risks, and user acceptance. The report emphasizes the importance of safe water storage and education to maximize health benefits.
more
The Our World in Data webpage on air pollution provides an extensive overview of the global impact of air pollution on health and the environment. It presents data on sources of pollution, such as industry, vehicles, and domestic energy use, and hig
...
hlights the associated health risks, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. The site emphasizes that air pollution is one of the leading environmental risk factors for premature deaths worldwide, particularly affecting low- and middle-income countries. It also discusses trends in air pollution levels over time and the effectiveness of policy interventions in reducing pollution and improving public health.
more
This website provides comprehensive guidance on vaccinations, malaria prevention and general health measures for travellers to tropical and developing regions. It emphasises two main vaccination criteria: the administrative requirements of the desti
...
nation country and the actual health risks to the traveller. Malaria prevention measures include chemoprophylaxis (e.g. atovaquone-proguanil, doxycycline or mefloquine) and vector control methods such as insecticide-treated nets, insect repellents and environmental protection measures. Additional travel health risks covered include bites from other arthropods, envenomations, dog and mammal bites, food and water hygiene, traveller's diarrhoea, and considerations for pregnant women, infants, the elderly, and people with chronic conditions. It strongly recommends carrying a travel medical kit and having a pre-travel consultation. Overall, the document aims to minimise illness and ensure safe travel.
Accessed on 27/08/2025.
more
Event-based surveillance (EBS) is defined as the organized collection, monitoring, assessment and interpretation of mainly unstructured ad hoc information regarding health events or risks, which may
...
represent an acute risk to health. Both indicator-based and event-based surveillance components serve the early warning and response (EWAR) function of the public health surveillance system. The Framework for Event-based Surveillance offers guidance to public health practitioners seeking to implement EBS at each administrative level in their countries.
more
Many migrants find themselves with limited access, if any, to information about risks, prevention measures, health care and other essential services. Migrants in transit, those in need of internatio
...
nal protection or without legal status are likely to be particularly vulnerable, as well as those who are homeless, held in detention, living in camps, formal or informal settlements or otherwise precarious conditions
more
Worldwide, there are about 17 million deaths due to cardiovascular disease (CVD) each year and at least two or three times as many non-fatal events. Raised cholesterol greatly increases the risks of stroke and heart disease, causing a large
...
health burden across the world. The World Health Organization has identified control of cholesterol as part of a Total Risk Approach to the prevention of CVD as a public health priority.
more
Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of mortality and reduced life expectancy. We aim to estimate the burden of diabetes by type, year, regions, and socioeconomic status in 195 countries and territories over the past 28 years, which provide information to achieve the goal of World
...
Health Organization Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in 2025. Data were obtained from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Overall, the global burden of diabetes had increased significantly since 1990. Both the trend and magnitude of diabetes related diseases burden varied substantially across regions and countries. In 2017, global incidence, prevalence, death, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) associated with diabetes were 22.9 million, 476.0 million, 1.37 million, and 67.9 million, with a projection to 26.6 million, 570.9 million, 1.59 million, and 79.3 million in 2025, respectively. The trend of global type 2 diabetes burden was similar to that of total diabetes (including type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes), while global age-standardized rate of mortality and DALYs for type 1 diabetes declined. Globally, metabolic risks (high BMI) and behavioral factors (inappropriate diet, smoking, and low physical activity) contributed the most attributable death and DALYs of diabetes. These estimations could be useful in policy-making, priority setting, and resource allocation in diabetes prevention and treatment.
more
The document presents Cameroon's National Response Plan for the 2018 cholera outbreak, covering August to October 2018. It highlights the epidemiological situation, with outbreaks reported in the North and Central regions and a total of 109 suspected cases and 9 deaths by July 2018. The plan outline
...
s strategies for controlling the epidemic, including epidemiological surveillance, improved access to clean water, sanitation, mass vaccination, community awareness campaigns, and hospital and community-based treatment.
The response is coordinated by the Ministry of Public Health, WHO, and various partners, focusing on early detection, rapid response, and multi-sectoral collaboration. Challenges include poor sanitation, limited healthcare infrastructure, and cross-border disease transmission risks. The plan emphasizes resource mobilization, monitoring, and evaluation to contain the outbreak and prevent future cases.
more
Buruli Ulcer, buruli ulcer signs and symptoms, buruli ulcer treatment, Buruli ulcer risks, Buruli ulcer disease, health care workers and buruli ulcer
This brief, rhythmic video uses a simple, memorable narrative to raise awareness of the dangers of malaria, emphasising how a mosquito bite can lead to serious health problems. The story follows someone who experiences malaria symptoms and seeks fre
...
e testing and treatment, emphasising the importance of early diagnosis and prompt medical care. The video's engaging message encourages viewers to avoid risks, get tested and receive appropriate treatment to prevent malaria from worsening.
more