Filter
24
Featured
Language
Document type
Studies & Reports
10
Guidelines
5
Strategic & Response Plan
3
Resource Platforms
2
Infographics
2
Videos
1
Fact sheets
1
Countries / Regions
Global
4
India
2
Asia
1
Africa
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Clinical Guidelines
1
Website last accessed on 08.06.2023
Website last accessed on 18.03.2023
GARC provides tools and training to build in-country skills and knowledge on essential elements of rabies control programmes, enabling countries to strengthen their efforts to eliminate rabies in a systematic way. Our most comprehensive in-country capacity bui
...
For more than 100 years, the clearest route to elimination of dog-mediated rabies has been via mass vaccination of the animal hosts. It’s worked in plenty of countries. Still, in others, like India, which grapples with a third of the world’s rabies burden, large populations of free-roaming, hard
...
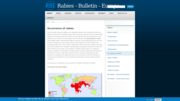
Classical rabies caused by RABV occurs worldwide besides some isolated countries and Western Europe that are regarded rabies free. Carnivores, especially of the canidae family represent the principal reservoir species and are responsible for the maintenance of the infectious cycle and hence for the
...
Rabies is fatal, vaccine-preventable disease responsible for an estimated 59,000 human deaths each year. Most cases are transmitted by dogs, and most deaths occur in underserved populations in Africa and Asia. Approximately 40% of deaths occur in children.
World Rabies Day is the biggest event on the global rabies calendar, coordinated by GARC and it has been commemorated every year on September 28 – the anniversary of the death of Louis Pasteur – since 2007. World Rabies Day aims to raise awareness and advocate for rabies elimination globally. It
...
Rabies is a fatal viral disease, but is preventable in humans. The rabies virus is transmitted to humans through virus-laden saliva from a rabid animal, mostly dogs. The virus is shed in the saliva of an infected animal and can be introduced into another body through bites, scratches and any other
...
Rabies is a fatal zoonotic disease most often transmitted to people via bites from infected dogs. This course provides a general introduction to rabies, and the One Health approach currently taken to prevent it. It consists of seven video-lectures, demonstration videos, and lessons learnt from peopl
...
Rabies is a virus (Lyssavirus) that infects cells in the central nervous
system, causing disease in the brain and, ultimately, death. Any animal
with rabies has the ability to transmit the disease to humans or other
animals.
There is no cure for rabies, but it is 100 percent preventable through
...
There is no cure for rabies, but it is 100 percent preventable through prompt, appropriate medical care. Every year hundreds of South Carolinians must undergo preventive treatment for rabies due to exposure to a rabid or suspected rabid animal. Although the cost varies, post-exposure treatment typic
...
Rabies is a viral zoonotic disease that causes progressive and fatal inflammation of the brain and spinal cord. Clinically, it has two forms:
Furious rabies – characterized by hyperactivity and hallucinations.
Paralytic rabies – characterized by paralysis and coma.
Rabies is a zoonotic, vaccine-preventable viral disease that causes damage to the brain and spinal
cord in infected animals and humans. A zoonotic disease is a disease that can be transmitted
between animals and humans. Rabies is nearly 100% fatal once symptoms appear.
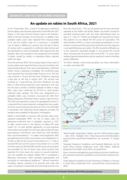
As of 14 December 2021, a total of 19 laboratory-confirmed human rabies cases has been reported in South Africa for 2021. The cases are from Eastern Cape, KwaZuluNatal and Limpopo provinces. In addition, four probable rabies cases were reported from KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern Cape provinces. A pr
...
Human rabies remains a significant public health problem in Africa with outbreaks reported in most countries. In Nigeria–the most populous country in Africa–rabies causes a significant public health burden partly due to perennial obstacles to implementing a national prevention and control progra
...
‘World Rabies Day’ is observed worldwide to mark the death anniversary of Louis Pasteur, a
French biologist, microbiologist and chemist who developed the first rabies vaccine. It’s a day where
Anti Rabies actions are collated, intensified and showcased.
Rabies is a neglected zoonotic disease responsible for an estimated 59,000 human deaths annually. Rural populations in Africa and Asia are predominantly affected, and approximately
40% of cases occur in children under the age of 15 years. Transmitted through bites and scratches from infected animal
...
Driving progress towards rabies elimination: Results of Gavi’s Learning Agenda on rabies and new WHO position on rabies immunization
2018 has been one of the most successful years ever for Mission Rabies. We are on
the cusp of having almost vaccinated one million dogs in global rabies hotspots,
we’ve educated over two million children and we’re seeing a dramatic reduction in
both human and canine rabies in all our flagship
...
Rabies is a viral infection of wild and domestic mammals, transmitted to humans by the saliva of infected animals through bites, scratches or licks on broken skin or mucous membranes.
In endemic areas (Africa and Asia), 99% of cases are due to dog bites and 40% of cases are children under 15 years
...
Video
Further OIE Support for African Countries on Rabies vaccines