Filter
19114
Filtered Results: 19114
Text search:
who
Featured
Recommendations
1620
New Publications
4349
Language
Document type
No document type
9538
Studies & Reports
3069
Guidelines
2412
Fact sheets
894
Manuals
884
Strategic & Response Plan
615
Training Material
399
Situation Updates
337
Infographics
296
Resource Platforms
240
Online Courses
135
Videos
126
Brochures
115
Dashboards/Maps
39
App
15
Countries / Regions
Global
912
India
705
Kenya
407
Sierra Leone
381
Liberia
339
South Africa
321
Ethiopia
321
Nigeria
320
Nepal
308
Uganda
300
Western and Central Europe
297
Latin America and the Carribbean
287
Syria
257
Myanmar / Burma
252
Africa
245
Russia
239
Rwanda
232
Congo, Democratic Republic of
232
Bangladesh
229
Ukraine
227
Tanzania
212
Malawi
208
Germany
206
Zambia
205
Indonesia
202
Ghana
172
Brazil
159
Namibia
158
Mozambique
148
Senegal
143
Guinea
138
Philippines
136
Eastern Europe
136
South Sudan
131
Yemen
129
Middle East and North Africa
124
West and Central Africa
122
Burkina Faso
114
Haiti
110
Zimbabwe
108
Lesotho
104
Venezuela
100
East and Southern Africa
99
South–East Asia Region
98
Cambodia
95
Asia
84
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
80
Colombia
73
Cameroon
73
Mali
64
Botswana
59
Lebanon
57
Angola
55
Central African Republic
53
Paraguay
52
Madagascar
52
Afghanistan
51
Pakistan
51
Eswatini/ Swaziland
49
Benin
48
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
47
Peru
46
Sudan
43
Somalia
43
China
38
Argentina
36
Niger
35
Vietnam
35
Jordan
34
Tajikistan
32
Guinea-Bissau
31
Western Pacific Region
30
Chad
29
Thailand
28
USA
28
Iraq
27
Ecuador
26
Turkey
25
Chile
25
Moldova
25
Sri Lanka
24
Bolivia
23
Spain
22
Togo
21
Albania
20
North America
19
Palestine
19
Laos
18
Burundi
15
Armenia
15
United Kingdom
15
Georgia
15
El Salvador
14
Iran
14
Portugal
14
Egypt
14
Libya
14
Kazakhstan
13
Mexico
12
Kyrgyzstan
12
Greece
12
North Macedonia
11
Saudi Arabia
11
Belarus
11
Papua New Guinea
11
Southern Africa
10
Romania
10
Honduras
10
Timor Leste/ East Timor
9
Italy
9
Guatemala
9
Serbia
8
Estonia
8
Uzbekistan
8
Malaysia
8
France
8
Tunisia
8
Poland
8
Gambia
7
Singapore
7
Hungary
7
Ireland
7
Jamaica
7
Bhutan
7
Japan
6
Switzerland
5
Canada
5
Congo-Brazzaville
5
Morocco
5
Dominican Republic
5
Turkmenistan
5
Azerbaijan
5
Nicaragua
5
Djibouti
5
Fiji
4
Mauritania
4
Gabon
4
Uruguay
4
North Korea
3
Australia
3
Vanuatu
3
Mongolia
3
Qatar
3
Croatia
3
Belgium
3
Mauritius
3
South Korea
3
Israel
3
Bosnia and Herzegovina
3
Guyana
3
Austria
2
Bulgaria
2
Lithuania
2
Denmark
2
Algeria
2
French Guyana
2
Slovakia
2
Solomon Islands
2
Cuba
2
Cape Verde
1
Luxembourg
1
Maldives
1
Norway
1
Morocco
1
Latvia
1
Barbados
1
Belize
1
Costa Rica
1
Eritrea
1
Oman
1
Panama
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Countries
6816
Clinical Guidelines
1173
Key Resources
947
Public Health
895
Women & Child Health
854
Capacity Building
405
Pharmacy & Technologies
173
Annual Report MEDBOX
3
Toolboxes
COVID-19
2398
Mental Health
1388
HIV
1182
TB
913
Ebola & Marburg
734
NTDs
711
Disability
710
Planetary Health
618
Conflict
531
Caregiver
510
AMR
472
NCDs
468
Refugee
464
Rapid Response
388
Global Health Education
317
Pharmacy
273
Natural Hazards
258
Malaria
252
Health Financing Toolbox
228
Zika
213
Cholera
177
2.0 Rapid Response
161
Social Ethics
115
Specific Hazards
106
Polio
106
Typhoon
12
South Sudan
2
Настоящий контрольный перечень позволит определить меры, которые необходимо реализовать для снижения риска передачи инфекции среди лиц, совершающих поездку, и со...
As of 30 June 2023, globally, a total of 24 countries reported AWD/cholera outbreaks. In the Eastern Mediterranean Region of WHO, 8 countries namely, Afghanistan, Iraq, Islamic Republic of Iran, Lebanon, Pakistan, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen have reported Acute Watery Diarrhea (AWD)/ suspected cholera...
The Health Systems in Transition (HiT) series consists of country-based reviews that provide a detailed description of a health system and of reform and policy initiatives in progress or under development in a specific country.
The meningitis road map has been designated as a flagship global strategy of the WHO’s Thirteenth General Programme of Work, 2019–2023 and is an essential component in achieving universal health coverage.
The road map will reinforce and combine with wider initiatives, such as those aimed at s...
Policy makers and public health professionals may be forced to weigh and prioritize potentially competing ethical values in the face of severe time and resource constraints. This video from the World Health Organisation explains that ethical concerns associated with the planning, preparedness and re...
Цель настоящего документа («Основные положения») заключается в подготовке рекомендаций относительно необходимых на национальном уровне мер по адаптации стратег�...
Mothers and healthcare workers who support them have many questions and concerns about whether it is safe for mothers with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 to be close to and breastfeed their babies during the pandemic.
To address their questions, WHO has released a list of Frequently asked question...
Transmission-based precautions for the prevention and control of infections: aide-memoire
recommended
Transmission-based precautions (TBP) are used in addition to standard precautions for patients with known or suspected infection or colonization with transmissible and/or epidemiologically significant pathogens. The type of TBP assigned to a patient depends on the transmission route of the microorga...
The COVID-19 Strategic Preparedness and Response Plan (SPRP) 2021 Monitoring and Evaluation Framework tracks global progress against the COVID-19 SPRP 2021 for the ten pillars of the public health response. The operational intelligence complements the epidemiologic information used to drive a global...
Updated with information on Ebola virus disease and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
A wide variety of health events ranging in severity may occur related to air transport, requiring different responses or, perhaps, no response at all. The target audience for this guidance document incl...
Principaux faits
D’après les estimations, 6 à 7 millions de personnes dans le monde sont infectées par Trypanosoma cruzi (T. Cruzi), le parasite responsable de la maladie de Chagas. La plupart de ces personnes vivent en Amérique latine.
La transmission à l’être humain se fait principalem...
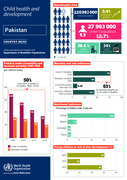
country brief, Pakistan
Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease, caused by monkeypox virus, recognized as the most important orthopoxvirus infection after the eradication of smallpox.
This course offers public health officers and health workers in-depth information to understand the epidemiology, modes of transmission, clin...
Le cancer du sein est le cancer le plus courant dans le monde et la première cause de mortalité imputable cette maladie chez les femmes. Il touche de façon disproportionnée les pays à revenu faible et intermédiaire. L’Initiative mondiale contre le cancer du sein met tout en œuvre pour faire...
As countries aim to progress towards the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and achieving universal health coverage, health inequities driven by racial discrimination and intersecting factors remain pervasive. Inequities experienced by indigenous peoples as well as people of African descent, Roma ...
Rabies is a vaccine-preventable, zoonotic, viral disease affecting the central nervous system. Once clinical symptoms appear, rabies is virtually 100% fatal. In up to 99% of cases, domestic dogs are responsible for rabies virus transmission to humans. Yet, rabies can affect both domestic and wild an...
-1-توصیاتللدول الأعضاء بشأن تحسین ممارسات نظافة الأیدي للمساعدة علىمنع انتقال فیروس كوفید-19
Despite the considerable improvement in global health, millions of people still lack access to quality health services, including access to effective antimicrobial medicines, or are impoverished as a result of health spending. At the same time, antimicrobial resistance – a consequence of overuse a...