Filter
2073
Text search:
antibiotics
Featured
257
531
Language
Document type
911
388
331
126
94
68
59
22
21
18
13
11
10
1
Countries / Regions
144
61
54
54
50
50
46
37
35
35
31
26
24
24
22
21
21
20
20
19
18
17
14
13
12
10
9
9
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
745
261
171
87
81
47
25
1
Toolboxes
428
104
99
90
86
82
51
50
42
39
37
36
32
29
25
20
18
15
15
13
12
12
4
2
1
The GEHM series is an evidence-informed normative product of the WHO
Health and Migration Programme to inform policy-makers on migrationrelated public health priorities. These reviews aim to respond to policy questions identified as priorities by summarizing the best available evidence worldwide an
...
The World Health Organization was requested by Member States to develop a global priority pathogens list (global PPL) of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to help in prioritizing the research and development (R&D) of new and effective antibiotic treatments. To date, the selection of pathogens for R&D ac
...
The systematic surveillance of antibiotic use and antibiotic re-sistance prevalence in humans and animals is imperative for managingbacterial infectious disease (JPIAMR, 2019;WHO, 2015). Many low-income countries currently face substantial challenges in building national surveillance systems due to
...
Nosocomial infections, or hospital-acquired infec-tions (HAI), are among the most significant causesof morbidity and mortality in healthcare settingsthroughout the world.Prevention of HAIs iscentral to providing high quality and safe health-care, even in settings with limited resources.Transmi
...
What have we learned about COVID-19 and antibiotics so far? What happens when antibiotics are not taken according to prescription or are used irrationally? When are
...
Phillips and colleagues have shown that rifampicin combined with clarithromycin is non-inferior to RS8, and is safer. This much anticipated trial provides us with a high degree of confidence that an 8-week course of oral rifampicin and clarithromycin should now be the cornerstone of the treatment of
...
Microbes like bacteria, fungus and viruses are becoming resistant to medicines like antibiotics. WHO has declared antimicrobial resistance as a global health and developmental threat. How can we stop antimicrobial resistance? Dr Hanan Balkhy explai
...
Accessed at March 2014
WHO commissioned a survey, carried out in September/October 2015, among some 10 000 members of the public in 12 countries (2 per WHO Region: Barbados, China, Egypt, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Nigeria, the Russian Federation, Serbia, South Africa, Sudan and Viet Nam) on their use of
...
Formularies are lists of antibiotics that are suggested for certain healthcare settings. In developing a recommended formulary, countries should consider the needs of patients and facilities where they receive care. For example, clinicians in rural
...
Of the 50 antibiotics in the pipeline, 32 target WHO priority pathogens but the majority have only limited benefits when compared to existing antibiotics. Two of these are active against the multi-d
...
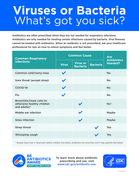
Antibiotics use with care
Antibiotics are only needed for treating certain infections caused by bacteria. Viral illnesses cannot be treated with antibiotics. When an antibiotic is not prescribed, ask your healthcare professi
...
Antibiotics save lives, but poor prescribing practices are putting patients at unnecessary risk for preventable allergic reactions,
super-resistant infections, and deadly diarrhea. Errors in prescribing decisions also contribute to antibiotic resis
...
Antibiotics have been a critical public health tool since the discovery of Penicillin in 1928, saving the lives of millions of people around the world. In developing country like ours, where the burden of treatable disease is very high and access to
...
Antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents are invaluable life savers, particularly in resource-limited countries where infectious diseases are abundant. Both uncomplicated and severe infections are potentially curable as long as the
...
Antibiotics, also known as antimicrobial drugs, are medicines that can kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria to cure infections in people, animals and sometimes plants. Antibiotics are medicines fo
...
Antibiotics have been useful in fighting infectious diseases in our country for decades, but because of the overuse and misuse of these agents, an increasing number of organisms are now resistant to them. The Philippines, like other Southeast Asian
...