Filter
1533
Text search:
AIDS
financing
Featured
108
516
Language
Document type
1011
257
89
83
49
17
10
6
5
2
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
98
69
49
44
44
43
39
38
38
36
32
32
31
30
29
28
26
26
23
21
21
19
19
16
14
13
13
12
12
9
9
9
8
8
7
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
696
84
58
53
42
9
7
1
Toolboxes
178
150
106
69
42
40
40
27
26
23
23
22
21
13
12
10
10
9
8
7
7
4
2
1
Countries are making progress toward the global goal of 95% of people living with HIV knowing their status by 2025. However, considerable gaps remain in achieving these goals globally. Men in high HIV burden settings and men from key populations in all settings are consistently less likely to know t
...
The Lancet HIV. Volume 12, Issue 10e712-e721October 2025. This article from The Lancet HIV estimates the impact of the PEPFAR funding pause for PrEP on HIV infections in sub-Saharan Africa.
A historic funding crisis is threatening to unravel decades of progress unless countries can make radical shifts to HIV programming and funding. The report highlights the impact that the sudden, large-scale funding cuts from international donors are having on countries most affected by HIV. Yet it a
...
A historic funding crisis is threatening to unravel decades of progress unless countries can make radical shifts to HIV programming and funding. The report highlights the impact that the sudden, large-scale funding cuts from international donors are having on countries most affected by HIV. Yet it a
...
Building true health security in a global age. Findings and recommendations of the Global Council. In landmark findings based on two years of research and convenings around the world, the new report shows that high levels of inequality are linked to outbreaks becoming pandemics and that inequality i
...
This publication discusses official development assistance (ODA) provided by the USA with a focus on health, HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis and malaria. It also reflects upon ODA by the USA in comparison to other donors and funding targets.
Diese Veröffentlichung befasst sich mit der öffentlichen Entwicklungshilfe (Official Development Assistance, ODA) der USA mit Schwerpunkt auf den Bereichen Gesundheit, HIV/AIDS, Tuberkulose und Malaria. Außerdem wird die ODA der USA im Vergleich
...
The findings of the report are both urgent and devastating. At the current rate of progress, by 2040 we would still have 1.9 million new HIV infections and 990,000 AIDS-related deaths in children. But if funding for HIV prevention and treatment cont
...
Recent suspensions and reductions in official development assistance (ODA) have posed significant challenges to HIV programme continuity in several countries. These funding disruptions have impacted people living with HIV and other vulnerable populations
who rely on these essential services, like a
...
This dataset contains data from WHO's data portal covering the following categories:
Air pollution, Antimicrobial resistance (AMR), Assistive technology, Child mortality, Dementia diagnosis, treatment and care, Dementia policy and legislation, Environment and health, Foodborne Diseases Estimates,
...
This report presents findings from research conducted by Economist Impact to assess the health, demographic, social and economic impacts associated with different scenarios for financing the HIV epidemic across 13 selected countries in Sub-Saharan A
...
Accessed on 28.02.2020
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated that
the world was not well prepared to respond
to an infectious disease threat of this magnitude. Countries across all socioeconomic and development categories have struggled
to implement effective national responses. Substantial amounts of additional investmen
...
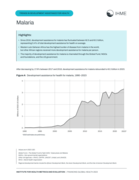
The document is part of the Financing Global Health 2023 series by the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) and focuses specifically on malaria. It provides a concise overview of global and regional trends in malaria-related health spe
...