Filter
9633
Text search:
risk
population
Featured
786
2524
Language
9147
330
206
154
95
69
47
38
15
11
11
8
7
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Document type
5080
1909
1137
507
383
274
141
110
33
31
12
7
1
1
1
Countries / Regions
443
400
259
207
187
186
186
184
184
182
173
156
140
133
131
130
126
126
121
119
110
105
101
85
76
72
72
71
70
69
67
66
65
64
62
57
56
52
50
50
48
47
45
42
41
40
39
35
32
32
31
31
30
26
25
24
23
23
23
21
20
18
17
17
17
16
15
15
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
10
10
9
9
9
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
1223
405
401
296
251
184
154
146
129
97
90
81
52
49
49
48
47
46
46
46
42
38
36
35
33
33
33
32
30
29
29
28
28
28
27
27
27
26
26
26
25
25
25
25
24
24
24
23
23
23
22
22
22
22
22
22
22
21
21
21
21
20
20
19
19
19
19
18
18
18
18
17
17
17
16
16
16
16
16
16
15
14
14
14
14
14
13
13
13
13
13
13
12
12
12
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Publication Years
1
3069
5819
706
34
3
1
Category
3735
609
569
506
476
158
65
3
Toolboxes
886
793
570
495
408
317
310
301
257
225
205
201
185
169
154
124
116
112
110
106
73
72
55
54
22
11
3
Lancet Public health 2022 January 6, 2022 https://doi.org/10.1016/ S2468-2667(21)00249-8
Growth in the number of individuals living with dementia underscores the need for public health planning efforts and policy to address the needs of this group. Country-level estimates can be used to inform nati
...
onal planning efforts and decisions. Multifaceted approaches, including scaling up interventions to address modifiable risk factors and investing in research on biological mechanisms, will be key in addressing the expected increases in the number of individuals affected by dementia.
more
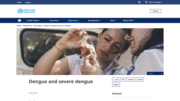
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral disease that has rapidly spread to all regions of WHO in recent years. Dengue virus is transmitted by female mosquitoes mainly of the species Aedes aegypti and, to a lesser extent, Ae. albopictus. These mosquitoes are also vectors of chikungunya, yellow fever and Zik
...
a viruses. Dengue is widespread throughout the tropics, with local variations in risk influenced by climate parameters as well as social and environmental factors.
more
Family planning: a global handbook for providers
recommended
4th edition 2022 of the Handbook includes new WHO recommendations that expand contraceptive choices. Also, guidance on starting ongoing contraception following emergency contraception is provided.
Drawing on lessons from recent outbreaks, this new edition details tangible me
...
asures for frontline health workers to protect access to family planning services during emergencies, such as wider access to self-administered contraceptives and the use of digital technologies by providers. It also expands guidance for women and young people at high risk of HIV.
more
Good practices from South & South-East Asia in disability inclusive disaster risk management
Cancer is an emerging public health problem in sub-Saharan Africa due to population growth, ageing and westernisation of lifestyles. In this piece, we use data from Mozambique over a 50-year period to illustrate cancer epidemiological trends in low
...
-income and middle-income countries to hypothesise potential circumstances and factors that could explain changes in cancer burden and to discuss surveillance weaknesses and potential improvements. This epidemiological transition deserves increasing policy attention.
more
The World Health Organization (WHO) endorses the use of population-based prevalence surveys for estimating the prevalence of trachoma. In general, the prevalence of TF in children aged 1–9 years and the prevalence of TT in adults aged ≥ 15 years
...
are measured at the same time in any district being surveyed. This was the approach of the Global Trachoma Mapping Project, which undertook baseline surveys in > 1500 districts worldwide in order to provide the data required to start interventions where needed.
The survey design recommended by WHO is a two-stage cluster random sample survey, which uses probability proportional to size sampling to select 20–30 villages, and random, systematic or quasi-random sampling to select 25–30 households in each of those villages. In most surveys, everyone aged ≥ 1 year living in selected households is examined. more
The survey design recommended by WHO is a two-stage cluster random sample survey, which uses probability proportional to size sampling to select 20–30 villages, and random, systematic or quasi-random sampling to select 25–30 households in each of those villages. In most surveys, everyone aged ≥ 1 year living in selected households is examined. more
West: Drada & Nagar Haveli, Daman & Diu, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra
South: Andhra Pradesh & Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu
This technical document consists of epidemiological profiles (fact-sheets) for States and districts based on information available from multiple d ... ata sources including the HIV Sentinel Surveillance (HSS) and the Integrated Biological and Behavioural Surveillance (IBBS). Given the need for focussed prevention efforts in low/high prevalence and vulnerable States/districts, the information presented will be useful for policy makers, program planners at national/State/ district level, researchers, and academicians in identification of areas for priority attention and also to derive meaningful conclusions for programme planning, implementation, monitoring and scale-up. This document will be a quick reference for the HIV/AIDS situation in a State/district, risk and safe behaviour of the high risk groups, their level of knowledge about STIs and HIV/AIDS, experience of violence, HIV testing and ART awareness and exposure to HIV/AIDS prevention. more
South: Andhra Pradesh & Telangana, Karnataka, Kerala, Puducherry, Tamil Nadu
This technical document consists of epidemiological profiles (fact-sheets) for States and districts based on information available from multiple d ... ata sources including the HIV Sentinel Surveillance (HSS) and the Integrated Biological and Behavioural Surveillance (IBBS). Given the need for focussed prevention efforts in low/high prevalence and vulnerable States/districts, the information presented will be useful for policy makers, program planners at national/State/ district level, researchers, and academicians in identification of areas for priority attention and also to derive meaningful conclusions for programme planning, implementation, monitoring and scale-up. This document will be a quick reference for the HIV/AIDS situation in a State/district, risk and safe behaviour of the high risk groups, their level of knowledge about STIs and HIV/AIDS, experience of violence, HIV testing and ART awareness and exposure to HIV/AIDS prevention. more
Northern: Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan, and Uttarakhand
Central: Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
Eastern: Andaman & Nicobar, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal
This technical document consists of epidemiological ... profiles (fact-sheets) for States and districts based on information available from multiple data sources including the HIV Sentinel Surveillance (HSS) and the Integrated Biological and Behavioural Surveillance (IBBS). Given the need for focussed prevention efforts in low/high prevalence and vulnerable States/districts, the information presented will be useful for policy makers, program planners at national/State/ district level, researchers, and academicians in identification of areas for priority attention and also to derive meaningful conclusions for programme planning, implementation, monitoring and scale-up. This document will be a quick reference for the HIV/AIDS situation in a State/district, risk and safe behaviour of the high risk groups, their level of knowledge about STIs and HIV/AIDS, experience of violence, HIV testing and ART awareness and exposure to HIV/AIDS prevention. more
Central: Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh
Eastern: Andaman & Nicobar, Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and West Bengal
This technical document consists of epidemiological ... profiles (fact-sheets) for States and districts based on information available from multiple data sources including the HIV Sentinel Surveillance (HSS) and the Integrated Biological and Behavioural Surveillance (IBBS). Given the need for focussed prevention efforts in low/high prevalence and vulnerable States/districts, the information presented will be useful for policy makers, program planners at national/State/ district level, researchers, and academicians in identification of areas for priority attention and also to derive meaningful conclusions for programme planning, implementation, monitoring and scale-up. This document will be a quick reference for the HIV/AIDS situation in a State/district, risk and safe behaviour of the high risk groups, their level of knowledge about STIs and HIV/AIDS, experience of violence, HIV testing and ART awareness and exposure to HIV/AIDS prevention. more
Policy Guidance Brief 2
• The potential health risks from climate change include: increase of waterborne and vector-borne diseases, heat-related illnesses, injuries and deaths, food insecurity and increased malnutrition. The poor, women, children and the elderly, as well as communities living ... in remote high-risk areas are most vulnerable.
• The expected results to achieve this outcome are: (i) climate risk management system is well-established, robust and nationally integrated to respond efectively to increased intensity and impact of risks and hazards on people’s health and wellbeing; (ii) improved social protection, gender consideration and risk finance capacity to prepare for and recover from potential loss and damage resulting from climate change; (iii) Myanmar’s health system is improved and can deal with climate-induced health hazards and support climate-vulnerable communities to respond effectively to disaster and health hazards from climate change. more
• The potential health risks from climate change include: increase of waterborne and vector-borne diseases, heat-related illnesses, injuries and deaths, food insecurity and increased malnutrition. The poor, women, children and the elderly, as well as communities living ... in remote high-risk areas are most vulnerable.
• The expected results to achieve this outcome are: (i) climate risk management system is well-established, robust and nationally integrated to respond efectively to increased intensity and impact of risks and hazards on people’s health and wellbeing; (ii) improved social protection, gender consideration and risk finance capacity to prepare for and recover from potential loss and damage resulting from climate change; (iii) Myanmar’s health system is improved and can deal with climate-induced health hazards and support climate-vulnerable communities to respond effectively to disaster and health hazards from climate change. more
This module carries pre-training entry level assessment as well as hands on exercise manual on Geographic Information Systems, Remote Sensing, Geographic Positioning System (GPS) and some applications of these technologies on Disaster Risk Managemen
...
t (DRM) especially for hazard mapping, monitoring and risk assessment module as well as the damage assessment module. Practical manual developed using open source products like Quantum GIS , RStudio, Google Earth Pro and Google Earth Engine.
This module can also can be used by other training facilitators, non-technical professionals and selflearners as well. However, it is strongly recommended that training participants and self-learners already have some basic knowledge of Computer Basic, Geoinformatics and disaster management.
No publication year indicated.
Original file: 30,5 MB more
This module can also can be used by other training facilitators, non-technical professionals and selflearners as well. However, it is strongly recommended that training participants and self-learners already have some basic knowledge of Computer Basic, Geoinformatics and disaster management.
No publication year indicated.
Original file: 30,5 MB more
Young children are especially susceptible to exposure to trauma. Rates of abuse and neglect among this population are staggering. This article presents a review of relevant literature, including research findings specific to early childhood vulnerab
...
ility to trauma, symptoms associated with traumatic events, diagnostic validity of early childhood trauma, and treatments for young children. In the past, misconceptions about the mental health of young children have hindered accurate diagnosis and treatment of trauma-related mental illness. Due to the prevalence of trauma exposure in early childhood, counselors are encouraged to become familiar with ways that clients and families are impacted and methods for treatment. Implications for future research also are presented.
more
Crisis Group’s Watch List identifies ten countries or regions at risk of deadly conflict or escalation thereof in 2021. In these places, early action, driven or supported by the EU and its member states, could enhance prospects for peace and stabi
...
lity.
Crisis Group’s early-warning Watch List identifies up to ten countries and regions at risk of conflict or escalation of violence. In these situations, early action, driven or supported by the EU and its member states, could generate stronger prospects for peace. The Watch List 2021 includes an Introduction, detailed conflict analyses and EU-targeted recommendations on Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, Iran & the Gulf, Libya, Mexico & Central America, Nagorno-Karabakh, Somalia, Thailand and Venezuela.
more
Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Children and Adolescents
Patrick, S., Perrin, S., Tim, D., Richard, M-S., David M, C., & William, Y.
Current Opinion in Psychiatry
(2013)
C1
Purpose of review: We review recent evidence regarding risk factors for childhood posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and treatment outcome studies from 2010 to 2012 including dissemination studies, early intervention studies and studies involving
...
preschool children.
more
Essential medicines are those that satisfy the priority health care needs of a population. They are selected with due regard to disease prevalence and public health relevance, evidence of efficacy and safety and comparative cost-effectiveness. They
...
are intended to be available in functioning health systems at all times, in appropriate dosage forms, of assured quality, and at prices individuals and health systems can afford.
more
HEARTS provides a set of locally adaptable tools for strengthening the
management of CVD in primary health care.
HEARTS is designed to enhance implementation of WHO PEN by providing:
• operational guidance on further integrating CVD management
• technical guidance on evaluating the impact of
...
CVD care on patient outcomes.
For countries not using WHO PEN, CVD management can still be integrated into
primary health care. The process of implementing HEARTS will vary, depending
on country context, and may require a significant reorienting and strengthening
of the health system. At some sites, existing CVD management services may be
reoriented toward a risk-based approach, while other sites may adopt a public
health approach, strengthening management of particular risk factors such as
hypertension. Whether or not introducing CVD management into primary care is a
new intervention, successful implementation will require engagement with national and local health planners, managers, service providers, and other stakeholders.
more
18 March 2020
WHO and public health authorities around the world are acting to contain the COVID-19 outbreak. However, this time of crisis is generating stress throughout the population. The considerations presented in this document have been dev
...
eloped by the WHO Department of Mental Health and Substance Use as a series of messages that can be used in communications to support mental and psychosocial well-being in different target groups during the outbreak.
more
Children living in humanitarian crises face an increased risk of abuse. While the threats of harm are increasing, the established systems in place to protect them are breaking down. Faced with the COVID-19 pandemic and its impacts, vulnerable famili
...
es suffer multiple hardships. Schools are closed and families have been pushed to the brink of poverty, sometimes having been denied the opportunity to protect and provide for their children.
The report provides an in-depth analysis of 19 Humanitarian Response Plans and Refugee Response Plans from 2019
more
In 2016, the risk of premature mortality1 from noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) in Ethiopia was 18.3%. The economic costs of NCDs are significant and are due principally to their impact on the non-health sector (reduced workforce and productivity). I
...
n this study, it is estimated that NCDs cost Ethiopia at least 31.3 billion birr (US$ 1.1 billion) per year, equivalent to 1.8% of the gross domestic product (GDP). Less than 15% of the costs are for health care.
more
8 February 2021
This document highlights 10 well established Risk Communication and Community Engagement (RCCE) principles that have proven their power. Together they put communities at the heart of the roll out of new vaccines, treatments and test
...
s and promote trust, the critical ingredient for all community action. Informed, engaged and empowered communities are the bedrock for the arrival of new vaccines, treatments and tests that will be introduced to reduce the spread of COVID-19 and save lives. With communities fully engaged and actively participating through the full cycle of planning, delivery and assessment for biomedical tools, demand for these tools can be increased, leading to widespread and effective uptake and use
more
Systematic screening for TB disease is the systematic identification of people at risk for TB disease, in a predetermined target group, by assessing symptoms and using tests, examinations or other procedures that can be applied rapidly.
Systematic
...
screening can benefit people who are at risk of getting TB, as early detection and start of treatment can improve their outcomes and reduce their costs. It can also benefit entire communities at higher risk for TB, by reducing the prevalence of TB disease and preventing future cases.
more