Filter
3270
Text search:
suspected
cases
Featured
446
875
Language
3150
82
68
48
37
33
15
12
6
5
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Document type
1614
730
390
197
121
83
64
50
6
5
5
2
1
1
Countries / Regions
208
141
137
112
87
73
73
68
63
60
56
51
51
42
42
41
39
38
37
33
32
32
32
30
29
29
28
27
24
22
21
21
20
20
20
20
18
18
17
16
14
14
13
12
12
12
12
11
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
567
178
100
94
73
56
47
47
36
35
32
30
27
26
24
21
19
19
16
15
14
14
14
14
13
13
12
12
12
12
11
11
11
11
11
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
10
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
8
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
7
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
6
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
5
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Publication Years
1152
1812
283
21
2
Category
1204
345
142
139
125
56
49
1
Toolboxes
546
301
217
164
138
113
82
78
75
72
70
69
57
55
52
49
48
36
32
29
28
20
12
5
4
1
1
Cloth masks and mask sterilisation as options in case of shortage of surgical masks and respirators
recommended
This document aims to provide advice on the use of cloth face masks and sterilisation of respirators and surgical masks as an alternative in healthcare settings with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 cases
...
if there is a shortage of specialised surgical masks and respirators.
more
19 August 2022. A monkeypox case investigation form (CIF) has been designed as a tool for Member States and researchers to conduct in-depth epidemiological investigation of suspected, probable and confirmed
...
cases of monkeypox. This form allows to collect data prospectively or retrospectively for both cases and their contacts. The full form is meant to serve as a tool for in-country use and the data are not required to be reported to WHO.
more
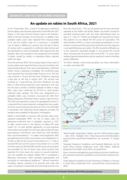
As of 14 December 2021, a total of 19 laboratory-confirmed human rabies cases has been reported in South Africa for 2021. The cases are from Eastern Cape, KwaZuluNatal and Limpopo provinces. In addi
...
tion, four probable rabies cases were reported from KwaZulu-Natal and the Eastern Cape provinces. A probable case of rabies is defined as a person who has had a history of contact with a suspected or confirmed rabid animal and has developed an acute encephalitis with hyperactivity and paralytic signs and symptoms that progressed and resulted in death, usually by cardiac or respiratory failure, typically within ten days.
more
As of 21 September, the diphtheria oubreak has resulted in a total of 453 deaths recorded among all confirmed cases (Case Fatality Rate/ CFR: 6.3%). A total of 11,587 suspected and 7,202 confirmed
...
cases have been reported with 99 local government areas (LGAs) affected across 18 states. Event has been categorized as Grade 2 Emergency, requiring moderate 3 level coordinated support to the Government Response.
more
Since the re-emergence of monkeypox in Nigeria in September 2017, the Nigeria Centre
for Disease Control(NCDC) has continued to receive reports and respond to cases of the
disease from States across the country. Between September 2017 when the out
...
break started and November 2018, about 300 suspected cases had been reported from 26 out of 36 states and the Federal Capital Territory. The highest number of cases were reported from States in the South-South region of Nigeria. Monkeypox is a zoonotic orthopox virus, which presents in humans with symptoms such as fever, headache, body pain, malaise, lymphadenopathy (enlargement of glands),
sore throat and the typical generalised vesiculopustular rash. Transmission is via direct or
indirect contact with infected animals, human, or contaminated materials.
more
The Ministry of Health (MoH) of Syria officially declared a cholera outbreak on 10 September 2022, with the majority of cases reported from Aleppo, Deir-ez-Zor and Al-Hasakeh governorates. Since the situation report issued on 26 September 2022, the
...
number of confirmed and suspected cases continues to rise. A total of 13 of 14 governorates are now affected, compared with 10 during the last reporting period.
more
The WHO Ebola Response Team presents new data on Ebola symptoms, case fatality rate, and incubation period, and experts discuss actions needed to deal with the oubreak. Stay informed with Perspective and research articles, an interactive
map of confirmed and
...
suspected cases, and links to the latest updates on the Ebola Outbreak
more
Situation analysis
Description of the disaster
An Ebola epidemic that started in March 2014 in Guinea has relentlessly continued to claim lives and to spread to other countries in West Africa. The current Ebola outbreak is the largest in history and the first to affect multiple countries simu
...
ltaneously. There have been over 24 000 reported confirmed, probable, and suspected cases of EVD in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone (table 1), with almost 10 000 reported deaths (outcomes for many cases are unknown). A total of 58 new confirmed cases were reported in Guinea, 0 in Liberia, and 58 in Sierra Leone in the 7 days to 8 March (4 days to 5 March for Liberia). Many experts believe that the official numbers substantially understate the size of the outbreak because of families' widespread reluctance to report cases. Because of the fluidity of movement of people between West Africa and several countries in the East African countries, especially Kenya and Ethiopia (who in turn have extensive interaction with other countries in the region in terms of human movement), the risk of an outbreak of Ebola in East Africa is as eminent as in any of the countries bordering the affected countries. The IFRC regional office intends to support National Societies to raise their Ebola preparedness and response capacity through training, technical support in planning and implementation of Ebola related activities, and coordination both within and outside the movement.
more
The report offers 20 top recommendations for getting ahead of future outbreaks in Yemen and similarly complex humanitarian settings.
In 2015, Yemen was declared a Level 3 emergency by the UN, kicking into gear the highest level of humanitarian support. A massive cholera outbreak followed, leading t
...
o 1 million suspected cases in 2 waves from September 2016-July 2018.
“We largely know ‘what to do’ to control cholera, but context-specific practices on ‘how to do it’ in order to surmount challenges to coordination, logistics, insecurity, access and politics remain needed,” the report states.
While the response improved between the 2 waves, there were gaps. For one, Yemen’s history of cholera should have triggered a heavy focus on pre-planning for an epidemic, such as stockpiling supplies and doubling down on community-based surveillance, the report fou
more
Most shelters in the Caribbean are community centers, schools, or churches that are limited in size. The novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) distancing requirements subsequently reduced the number of persons a shelter can accommodate during the hurricane season. This document reinforces some measur
...
es to follow per international emergency shelter protocols factoring in conditions for spacing between beds/cots, recreation areas and ventilation according to The Sphere Handbook, FEMA, and Australian Red Cross. Physical distancing and hygienic standards were modified highlighting that ideal requirements are not always feasible; therefore, we may choose realistic recommendations for practical purposes and suspected cases of COVID-19.
more
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) declared a Yellow Fever (YF) outbreak and activated a multi-sectoral Emergency Operations Centre for coordination of Yellow Fever response on 12 November 2020. The outbreak, which mainly affected three states of Delta, Enugu and Bauchi, already recorded
...
a total of 222 suspected cases 19 confirmed cases and 76 deaths between 1 and 11 November 2020.
more
After years of relative calm, Zimbabwe has been grappling with a cholera outbreak since 12 February 2023. This resurgence is not an isolated incident, as 10 more countries (Malawi, Mozambique, Somalia, Kenya, Ethiopia, Zambia, South Sudan, Burundi, Tanzania and South Africa) in Eastern and Southern
...
Africa are facing similar challenges with cholera an acute watery diarrhea.
To date, a total of 13,176 suspected cases and 1,543 confirmed cases have been reported.This stark reality underscores the need for continued coordinated action to control the spread of this preventable disease.
more
This guidance synthesizes current evidence on dengue laboratory testing and diagnostics and provides practical recommendations for laboratories, clinicians, public health officials, and programme managers involved in dengue diagnosis, surveillance, and control, in the context of the global emergency
...
. It includes a diagnostic algorithm for suspected cases, outlining appropriate testing methods based on days post symptom onset.
more
In December 2019 a novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) was identified as the causative agent of a severe acute respiratory illness among people exposed in a seafood market in Wuhan, China; • Human-to-human transmission has been documented, including in healthcare workers, and aerosol-generating procedur
...
es (AGP)† may play a role in the spread of the disease; • There are uncertainties in the natural history of the 2019-nCoV, including source(s), transmissibility mechanisms, viral shedding, and persistence of the virus in the environment and on fomites; • As of 6 February 2020, the following precautions are recommended for the care of patients with suspected or confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV: o For any suspected or confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV: standard + contact + droplet precautions o For any suspected or confirmed cases of 2019-nCoV and AGP: standard + contact + airborne precautions • The use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by healthcare workers requires an evaluation of the risk related to healthcare-related activities;
more
As of 30 June 2023, globally, a total of 24 countries reported AWD/cholera outbreaks. In the Eastern Mediterranean Region of WHO, 8 countries namely, Afghanistan, Iraq, Islamic Republic of Iran, Lebanon, Pakistan, Somalia, Syria, and Yemen have reported Acute Watery Diarrhea (AWD)/
...
suspected cholera cases during 2022. In 2023, 6 out of these 8 countries continued to report AWD/ suspected cholera cases in 2023.
more
The Manual for Parasitological Surveillance in Prevention of Reintroduction or Re-establishment of Malaria in Sri Lanka (2019) provides guidelines to health professionals on how to conduct effective malaria surveillance to prevent the reintroduction of the disease in Sri Lanka, which was certified m
...
alaria-free in 2016.
The manual outlines strategies for active and passive case detection, laboratory diagnosis, case investigation, foci investigation, and follow-up measures. It emphasizes targeted screening of high-risk populations, including travelers and migrant workers, and explains the importance of prompt reporting, accurate parasitological confirmation, and coordination between healthcare levels. The overall goal is to maintain Sri Lanka’s malaria-free status by ensuring early detection and rapid response to any imported or locally suspected malaria cases.
more
Ebola: Infection Prevention and Control for Health Care Workers in Community and Health Care Settings
WiRed International
(2015)
Ebola infections among health care providers can have devastating effects on individuals, on health care systems and on the communities they serve. This module discusses WHO and CDC infection prevention and control measures that health care facilities should follow to prepare for and to contain an i
...
nfectious disease outbreak. The module covers infection prevention and control (IPC) in a community and health care setting and looks at IPC in general patient care and in the care of suspected or confirmed cases of Ebola. The module also reviews environment cleaning and the management of linen and waste. Finally the module reviews non-patient care activities, such as IPC in burial procedures, and offers a comprehensive final quiz to help users confirm their understanding of the material.
more
Infection prevention and control practices need to be implemented to guarantee the safety of healthcare workers and patients in healthcare settings, it is fundamental to prevent cross contamination and containment of spread of COVID 19. As of the day of this publication, the following precautions ar
...
e recommended for the care of patients with suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19: - For any suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19: standard + contact + droplet precautions. -For any suspected or confirmed cases of COVID-19 and Aerosol Generated Procedure: standard + contact + airborne precautions. - The results of the application of this evaluation tool, in addition to other tools, will provide an overview regarding compliance with the activities of prevention and control of infections associated with provision of care in acute healthcare services in a health setting, without making judgments about the individual risk of patients, nor on particular cases. By its nature, this tool is only an external diagnostic to support IPC professionals and managers to assess the gaps and take corrective measures. To provide a tool for assessment of infection prevention and control practices in isolation areas in acute healthcare settings in the context of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19). These recommendations are preliminary and subject to review as new evidence becomes available.
more
In Yemen, the poorest country in the Middle East, 3 million children have been born into horrific violence that has escalated since March 2015.
Calling for the needs of Yemen’s children to be prioritized, UNICEF’s “Born into War” report reminds involved parties of their legal obligations t
...
o protect children during conflict—delivering a wake-up call backed by sobering statistics.
5,000 children have been killed or injured in the violence; over 11 million require humanitarian assistance. With the collapse of basic services, schools are closing and disease is spreading. Children under 5 account for a quarter of suspected cholera and acute watery diarrhea cases, which have afflicted over 1 million people.
more
According to the report:
More than 5,000 children have been killed or injured in the violence – an average of five children every day since March 2015.
More than 11 million children now need humanitarian assistance – nearly every child in Yemen.
More than half of the country’s
...
children don’t have access to safe drinking water or adequate sanitation.
An estimated 1.8 million children are acutely malnourished, including nearly 400,000 severe acutely malnourished children who are fighting for their lives.
Nearly 2 million children are out of school, including almost half a million who dropped out since the conflict escalated in March 2015.
Suspected cholera and acute watery diarrhea have affected over 1 million people, with children under 5 years old accounting for a quarter of all cases.
more