Filter
720
Text search:
National
systems
response
to
NCDs
Featured
Recommendations
66
New Publications
188
Language
Document type
No document type
302
Studies & Reports
223
Guidelines
82
Strategic & Response Plan
56
Manuals
37
Situation Updates
6
Fact sheets
6
Training Material
5
Resource Platforms
3
Countries / Regions
Global
82
Kenya
32
Malawi
20
South Africa
19
India
18
Latin America and the Carribbean
18
Liberia
17
Rwanda
17
Ukraine
16
Africa
15
Ethiopia
14
Zambia
14
Ghana
13
Namibia
13
Western and Central Europe
13
Uganda
12
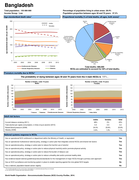
Bangladesh
12
South–East Asia Region
12
Philippines
11
Nigeria
10
Tanzania
10
Myanmar / Burma
10
Sierra Leone
9
Nepal
9
Syria
7
Lesotho
6
Asia
6
Cambodia
5
Botswana
5
East and Southern Africa
5
Middle East and North Africa
5
Western Pacific Region
5
Eastern Europe
5
Zimbabwe
4
Indonesia
4
Yemen
4
West and Central Africa
4
North America
4
South Sudan
3
Mozambique
3
Eswatini/ Swaziland
3
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
3
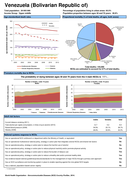
Venezuela
3
Russia
3
Senegal
2
Pakistan
2
Turkey
2
Thailand
2
Sudan
2
Colombia
2
Mexico
2
Bulgaria
2
Moldova
2
Kyrgyzstan
2
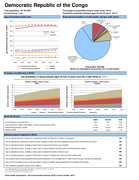
Congo, Democratic Republic of
1
USA
1
Saudi Arabia
1
Cameroon
1
Haiti
1
Somalia
1
Iraq
1
Jordan
1
Afghanistan
1
Lebanon
1
Egypt
1
Chad
1
China
1
Argentina
1
Peru
1
Brazil
1
North Macedonia
1
Hungary
1
Bolivia
1
Madagascar
1
Chile
1
Other region
1
Paraguay
1
Poland
1
Albania
1
Laos
1
Timor Leste/ East Timor
1
Tajikistan
1
Romania
1
Slovakia
1
Kazakhstan
1
Vietnam
1
Jamaica
1
Japan
1
Mauritius
1
United Kingdom
1
Portugal
1
Spain
1
Israel
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Countries
348
Public Health
127
Clinical Guidelines
65
Women & Child Health
24
Key Resources
22
Capacity Building
7
Pharmacy & Technologies
6
Toolboxes
NCDs
103
Mental Health
57
Planetary Health
46
COVID-19
44
Global Health Education
26
HIV
23
Conflict
22
Caregiver
16
Health Financing Toolbox
15
Disability
12
TB
11
Refugee
6
2.0 Rapid Response
4
Natural Hazards
3
Rapid Response
3
Pharmacy
3
NTDs
3
AMR
2
Ebola & Marburg
1
Cholera
1
Social Ethics
1
Malaria
1
Socioeconomic status is associated with differences in risk factors for cardiovascular disease incidence and outcomes, including mortality. However, it is unclear whether the associations between cardiovascular disease and common measures of socioeconomic status—wealth and education—differ among
...
The document "Diabetes and Ramadan: Practical Guidelines 2021," published by Elsevier, provides updated guidance for managing diabetes during Ramadan fasting. Developed by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) and the Diabetes and Ramadan (DAR) International Alliance, the guidelines address ke
...
As Uganda builds back from the COVID-19 shock, the Ugandan government is strengthening its commitment to a more gender-inclusive and sustainable economy. This report supports these efforts by describing the gendered impacts of COVID-19 and provides
...
Hypertension is the number one health related risk factor in India, with the largest contribution to burden of disease and mortality. It contributes to an estimated 1.6 million deaths, due
...
The Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD) began 30 years ago with the goal of providing timely, valid and relevant assessments of critical health outcomes. Over this period, the GBD has become progressively more granular. The latest iteration provides assessments of thousands of outcomes for diseases
...
Diabetes mellitus, also called diabetes, is a chronic metabolic condition in which the hormone insulin is not produced by the
pancreas in sufficient quantities or is not utilized effectively by the body to control blood glucose levels. As a result,
...
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by the presence of hyperglycaemia in the absence of treatment. The heterogeneous aetiopathology includes defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. The long-term specific complications of diabe
...
Unmet mental health needs in the Region of the Americas are a leading source of morbidity and mortality, which result in tremendous health, social, and economic consequences. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the mental health crisis in the Region, necessitating urgent action at the highest leve
...
Background
Low- and middle-income countries now experience the highest prevalence and mortality rates of cardiovascular disease.
Main text
While improving the availability and delivery of proven, effective therapies will no doubt mitigate this burden, we posit that studies evaluating cardiovasc
...
Alcohol use is deeply embedded in the social landscape of many societies, and some 2300 million people drink alcoholic beverages in most parts of the world. At the same time, more than half of the global population aged 15 years and older reported having abstained from drinking alcohol during the pr
...
In 2012, 25.7% of adults in Tanzania aged 25–64 had hypertension, affecting approximately 4 million people. However, most remain unaware of their condition or are not receiving treatment, with only 0.1 million achieving blood pressure control.
In 2015, 23.7% of Kenyan adults aged 18–69 — around 5.7 million people — had hypertension. However, only 0.2 million of these individuals had their condition under control. Awareness and treatment rates remain low.
The Lancet Published Online September 13, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31404-0