Filter
7628
Filtered Results: 7628
Text search:
medical
education
Featured
Recommendations
623
New Publications
1987
Language
Document type
No document type
4500
Studies & Reports
1203
Guidelines
808
Manuals
394
Strategic & Response Plan
268
Training Material
145
Fact sheets
124
Situation Updates
79
Infographics
30
Brochures
29
Resource Platforms
28
Online Courses
11
Videos
8
App
1
Countries / Regions
India
369
Kenya
291
Global
272
South Africa
193
Nepal
163
Ethiopia
163
Uganda
160
Sierra Leone
158
Nigeria
144
Tanzania
144
Liberia
136
Western and Central Europe
133
Zambia
129
Myanmar / Burma
126
Bangladesh
123
Rwanda
111
Malawi
110
Ghana
99
Syria
97
Africa
94
Namibia
84
Ukraine
83
Latin America and the Carribbean
82
Congo, Democratic Republic of
81
Philippines
65
Senegal
58
Zimbabwe
57
Haiti
57
Lesotho
55
Cambodia
52
Mozambique
50
Burkina Faso
45
Asia
45
Eastern Europe
45
Indonesia
45
Germany
44
South Sudan
43
South–East Asia Region
42
Guinea
35
West and Central Africa
35
Botswana
35
Venezuela
34
Brazil
33
East and Southern Africa
32
Benin
31
Eswatini/ Swaziland
31
Cameroon
28
Russia
28
Middle East and North Africa
26
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
23
Lebanon
23
Yemen
23
Colombia
22
Afghanistan
22
Central African Republic
22
Vietnam
20
Pakistan
20
Jordan
19
Thailand
17
Sudan
17
Madagascar
17
Western Pacific Region
15
Mali
15
China
14
USA
14
Somalia
13
Tajikistan
12
Moldova
12
Laos
11
Iraq
11
Albania
10
Sri Lanka
10
Paraguay
9
Georgia
9
Angola
9
Iran
8
Peru
8
North Macedonia
7
Turkey
7
Chile
7
Niger
7
Greece
7
Palestine
7
Togo
6
Burundi
6
North America
6
United Kingdom
6
Southern Africa
6
Papua New Guinea
6
Poland
6
Libya
6
Kazakhstan
5
Portugal
5
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
5
Bolivia
5
Argentina
5
Egypt
5
Romania
5
Ecuador
5
Timor Leste/ East Timor
4
Canada
4
Honduras
4
Bhutan
4
Guatemala
4
Mexico
3
El Salvador
3
Serbia
3
Singapore
3
Estonia
3
Kyrgyzstan
3
Malaysia
3
Armenia
3
Guinea-Bissau
3
Hungary
3
Jamaica
3
Japan
3
Mauritius
3
Gambia
2
Fiji
2
Morocco
2
Bulgaria
2
Dominican Republic
2
Croatia
2
Lithuania
2
Saudi Arabia
2
Turkmenistan
2
Spain
2
Nicaragua
2
Slovakia
2
Chad
2
Switzerland
1
Australia
1
Uzbekistan
1
Austria
1
Mongolia
1
Qatar
1
Italy
1
Ireland
1
Gabon
1
France
1
Maldives
1
Tunisia
1
South Korea
1
Belarus
1
Israel
1
Latvia
1
Belize
1
Costa Rica
1
Panama
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Countries
3224
Clinical Guidelines
450
Public Health
417
Women & Child Health
388
Key Resources
358
Capacity Building
163
Pharmacy & Technologies
38
Annual Report MEDBOX
3
Toolboxes
Mental Health
696
HIV
531
COVID-19
531
Disability
400
TB
302
Caregiver
254
Conflict
221
AMR
217
Ebola & Marburg
183
Refugee
172
Planetary Health
168
NCDs
164
NTDs
157
Rapid Response
153
Global Health Education
130
Pharmacy
106
Natural Hazards
85
Malaria
64
Health Financing Toolbox
63
Cholera
42
Social Ethics
36
Specific Hazards
34
Zika
27
Polio
23
2.0 Rapid Response
21
Typhoon
4
South Sudan
1
Including Therapeutic Food, Dietary Vitamin and Mineral Supplementation - 2nd edition
Accessed 13 Febr 2015
A report submitted to the International Labour Organization, Geneva
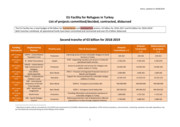
The EU Facility has a total budget of €6 billion for humanitarian and development actions: €3 billion for 2016-2017 and €3 billion for 2018-20191. Both tranches combined, all operational funds have been committed, €4.7 billion contracted and more than €3.4 billion disbursed. The operationa...
Open Journal of Psychiatry, 2014, 4, 390-395
Published Online October 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojpsych
http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojpsych.2014.44045
Interim Guidance 18th March 2020
In line with the National Mental Health Strategy for Lebanon (2015-2020), this guide answers the objective of the Mental Health and Psychosocial Support task force: “Development and provision of staff care interventions for persons working in the MHPSS and Protection sectors”. It aims at prevent...
The case studies in this document are set in different scales and geographies, tackling a wide realm of issues connected to urban housing recovery — locally in Nepal and globally. The case studies are categorized into three:
case studies from partner organizations
case studies from house...
Manual with Scale
Health care-associated infections (HAI) are one of the most common adverse events in care delivery and a major public health problem with an impact on morbidity, mortality and quality of life. At any one time, up to 7% of patients in developed and 10% in developing countries will acquire at least on...
This update of the Guidelines for poison control, entitled Guidelines for establishing a poison centre, reflects the development of the role of poison centres in public health and the sound management of chemicals, described in section 1, and the opportunities provided by new technology. Assessments...
Guidelines
Key Populations
Selection and Use of Essential Medicines 2021
recommended
The 23rd meeting of the WHO Expert Committee on Selection and Use of Essential Medicines was coordinated from Geneva, Switzerland, and held virtually from 21 June to 2 July 2021. The Committee considered 88 applications proposing additions, changes and deletions of medicines, medicine classes and fo...
Produced by UNICEF and IRC, with the support of the German Corporation for International Cooperation GmbH (GIZ) and the generous funding from the German Federal Ministry of Economic Cooperation and Development (BMZ), the Caring for Child Survivors of Sexual Abuse (CCS) Resource Package (Second Editi...