Filter
28597
Filtered Results: 28597
Text search:
a
Featured
Recommendations
2158
New Publications
6389
Language
Document type
No document type
13893
Studies & Reports
4082
Guidelines
3192
Fact sheets
1520
Manuals
1113
Resource Platforms
881
Infographics
841
Strategic & Response Plan
773
Training Material
602
Situation Updates
521
Videos
506
Brochures
295
Online Courses
270
Dashboards/Maps
81
App
27
Countries / Regions
Global
1427
India
989
Germany
916
Sierra Leone
521
Kenya
515
Congo, Democratic Republic of
500
Liberia
454
South Africa
442
Latin America and the Carribbean
440
Nepal
436
Nigeria
425
Russia
421
Ukraine
411
Ethiopia
406
Senegal
387
Western and Central Europe
377
Africa
372
Uganda
349
Syria
342
Myanmar / Burma
332
Indonesia
319
Brazil
317
Guinea
315
Rwanda
304
Burkina Faso
301
Bangladesh
294
Tanzania
288
Haiti
270
Venezuela
266
Mozambique
264
Malawi
259
Zambia
243
Yemen
221
Ghana
217
Eastern Europe
205
Paraguay
201
South Sudan
197
Colombia
195
West and Central Africa
190
Philippines
182
Middle East and North Africa
181
Namibia
178
Mali
168
Argentina
157
Benin
156
East and Southern Africa
148
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
144
Peru
139
Cameroon
137
Zimbabwe
130
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
125
Lesotho
114
Cambodia
112
South–East Asia Region
112
Asia
107
Angola
106
Central African Republic
104
Madagascar
103
Niger
94
Chile
90
Guinea-Bissau
84
Botswana
81
Bolivia
76
Chad
75
Lebanon
72
Somalia
72
Ecuador
71
Afghanistan
67
Pakistan
64
Eswatini/ Swaziland
61
Spain
54
Sudan
51
USA
49
China
47
El Salvador
46
Vietnam
44
Togo
41
Jordan
40
Iraq
40
Tajikistan
39
Thailand
36
Turkey
36
Western Pacific Region
34
Italy
33
North America
32
Portugal
31
Mexico
30
Switzerland
27
Canada
27
Moldova
27
Sri Lanka
27
Egypt
27
United Kingdom
25
Albania
24
Burundi
24
Singapore
23
Laos
22
Palestine
21
Kazakhstan
20
Iran
20
Honduras
20
Guatemala
20
Kyrgyzstan
18
Armenia
18
Saudi Arabia
18
France
18
Georgia
18
Greece
17
Libya
17
Malaysia
15
Papua New Guinea
14
North Macedonia
13
Dominican Republic
13
Belarus
13
Uzbekistan
12
Morocco
12
Southern Africa
12
Estonia
11
Congo-Brazzaville
11
Austria
11
Uruguay
11
Djibouti
11
Gambia
10
Ireland
10
Tunisia
10
Nicaragua
10
Romania
10
Poland
10
Timor Leste/ East Timor
9
Serbia
9
Hungary
9
Luxembourg
9
Algeria
9
Mauritania
8
Japan
8
Jamaica
7
Bhutan
7
Cuba
7
Turkmenistan
6
North Korea
5
Gabon
5
Belgium
5
South Korea
5
Azerbaijan
5
Australia
4
Fiji
4
Vanuatu
4
Mongolia
4
Croatia
4
Qatar
3
Cape Verde
3
Denmark
3
Mauritius
3
Israel
3
Bosnia and Herzegovina
3
Guyana
3
Bulgaria
2
Lithuania
2
Maldives
2
French Guyana
2
Latvia
2
Slovakia
2
Solomon Islands
2
Norway
1
Morocco
1
Slovenia
1
Barbados
1
Belize
1
Costa Rica
1
Eritrea
1
Oman
1
Panama
1
United Arab Emirates
1
Bahamas
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Countries
10528
Clinical Guidelines
1442
Public Health
1282
Key Resources
1236
Women & Child Health
1158
Capacity Building
626
Pharmacy & Technologies
225
Annual Report MEDBOX
5
Toolboxes
COVID-19
3933
Mental Health
1900
Refugee
1369
HIV
1284
Ebola & Marburg
1263
TB
1218
NTDs
1190
Disability
878
Planetary Health
873
NCDs
864
Caregiver
737
Conflict
720
Rapid Response
711
AMR
607
Global Health Education
440
Malaria
429
Natural Hazards
399
Health Financing Toolbox
359
Pharmacy
349
Zika
348
Cholera
340
Specific Hazards
147
Social Ethics
147
Polio
141
2.0 Rapid Response
98
Typhoon
26
South Sudan
3
Tanzania WASH sector stakeholders collaborated between March and May 2022 to develop this Country WASH M&E Roadmap. The initial vision, outcomes and activities outlined in the Roadmap were established during a workshop, held on 2–3 March 2022, and further refined during a second workshop, held on ...
Emergency medicine in Rwanda is underdeveloped. Limited training and infrastructure mean that the country has a high mortality rate from acute conditions such as trauma, malaria and obstetric complications. As Rwanda's disease burden shifts, there is a critical need for standardised emergency care. ...
In order to contribute especially to the achievement of Target (g) of the Sendai Framework, several international and regional organizations as well as national institutions with a key role in early warning joined forces and established the International Network for Multi-Hazard Early Warning System...
Early warning systems are an essential tool for risk management and disaster preparedness that help save lives and minimize the potential impact of disasters. To be effective, early warning systems need to rely on the direct participation of at-risk communities, facilitate public education and aware...
This guide aims to provide an overview of successful practice from the field for the disaster risk reduction/management practitioner interested in EWS. It presents guiding principles that will build a strong foundation for the design or strengthening of EWS at any level. It is not an operational, bu...
The Training Toolkit for Community Early Warning Systems is an operational manual that aims to strengthen early warning systems in a developing country context. It accompanies and should put into practice the guiding strategic principles found in the Community Early Warning Systems: Guiding Principl...
The 2024 edition reviews more than 50 health-related indicators from the Sustainable Development Goals and WHO’s Thirteenth General Programme of Work. It also highlights the findings from the Global health estimates 2021, notably the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on life expectancy and healthy l...
The “RRT Training Programme” (RRT TP) is a structured collection of learning resources including learning materials, guidance, and tools enabling Member States to plan, implement and evaluate customized training for RRT managers and RRT members at national and subnational levels. This programme ...
The World Health Organization recently redefined leprosy elimination as a phased process, with the first milestone being the
interruption of transmission, achieved when no new child cases (defined as younger than 15 years) are reported for five consecutive years.
In Pakistan, the well-functioning ...
Growing emergencies and displacements across the world demand increasingly complex interventions and responses. The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed Malaria control in emergencies: a field manual to provide technical guidance to help partners respond effectively to malaria in emergency ...
Despite being a preventable and curable infectious disease, tuberculosis (TB) has continued to elude global controll efforts. In 2023, 8.2 milion people with TB were diagnosed and notified to the WHO, the hightest number ever reported since WHO began tracking.
Breastfeeding is a cornerstone of healthy infant nutrition, development and survival. It is critical for countries* to improve breastfeeding rates in order to achieve global targets for newborn and child health and survival, as well as economic growth and environmental sustainability
Noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) are chronic medical conditions that are not spread from person to person. Unlike infectious diseases, which are caused by bacteria, viruses, or other pathogens, NCDs are typically long-lasting and result from a combination of genetic, physiological, environmental, and...
How can we eradicate malaria? Explore cutting-edge science and technology, and examine policies needed, to control and eliminate malaria.
The number of global reported natural disaster events in any given year. Note that this largely reflects increases in data reporting, and should notbe used to assess the total number of events.
Accessed: 14.03.2019
DNDi’s long-term goal for sleeping sickness, also known as human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), is to develop and register two new drugs that are effective against both Stage 1 and Stage 2 of the disease and both subspecies of the parasite, T.b. gambiense and T.b. rhodesiense. T.b. rhodesiense is ...
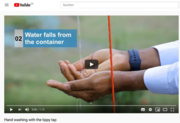
Hand washing with the tippy tap
recommended
Hand washing is one of the best ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19. But not everyone has access to running water at all times. The tippy tap is one simple and safe way to wash your hands that is especially designed for areas with no running water
World Health Organization. Regional Office for South-East Asia
To help improve understanding of an emerging outbreak’s complex dynamics, GHN has reached out to some of the world’s most respected global health experts for their quick "reality checks" on key issues related to the outbreak.