Filter
772
Text search:
cholera
outbreak
Featured
113
274
Language
Document type
334
123
106
71
43
37
24
19
7
6
2
Countries / Regions
46
37
34
28
23
23
23
23
20
17
17
17
16
15
15
12
11
11
10
9
9
8
8
8
8
7
7
7
6
6
6
5
4
4
4
4
3
3
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
304
106
53
38
27
11
5
1
Toolboxes
144
61
57
53
47
34
30
29
24
15
13
11
10
6
6
6
5
5
3
3
2
1
1
1
Cholera is an acute diarrhoeal infection caused by ingestion of contaminated water or food.
This introductory-level course has 4 sections and is intended for personnel responding to cholera outbrea
...
This document aims to provide advice on the detection and management of ill travellers suspected of COVID-19 infection, at international airports, ports and ground crossings. It includes the following measures; 1)Detection of ill travellers; 2) Interview of ill travellers for COVID-19; 3) Reporting
...
El documento es una guía de bolsillo para establecer y operar un Centro de Tratamiento de Cólera (CTC). Proporciona pautas para seleccionar la ubicación, clasificar a los pacientes según la gravedad de la deshidratación, implementar medidas de control de infecciones y garantizar el suministro a
...
A cólera é uma infecção intestinal provocada por uma bactéria conhecida como Vibrio cholerae. Os principais sintomas desta doença são diarréia e vômitos. Transmissão de cólera ocorre principalmente pelo consumo de alimentos contaminados ou água potável. Neste vídeo descrevemos várias
...
La respuesta a los brotes de cólera suele centrarse en los aspectos médicos que son importantes para que disminuya la mortalidad. Sin embargo, para limitar la propagación de la enfermedad se necesita una respuesta más integral. Dado que la respuesta a los brotes a menudo la dirigen profesionales
...
A resposta a um surto de cólera focaliza geralmente os aspectos médicos que são importantes para reduzir a mortalidade. Contudo, há necessidade de uma resposta mais abrangente para limitar a propagação da doença. Como a resposta a surtos é geralmente dirigida por profi ssionais médicos, pod
...
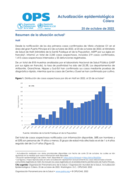
Desde la notificación de los dos primeros casos confirmados de Vibrio cholerae O1 en el área del gran Puerto Príncipe el 2 de octubre de 2022, al 23 de octubre de 2022, el Ministerio de Salud de Haití (Ministère de la Santé Publique et de la Population, MSPP por sus siglas en francés), inform
...
The Facilitator Training Manual on Workplace Pandemic Preparedness is a guide developed by GIZ and the Ministry of Health to help organizations prepare for and respond to pandemics while ensuring business continuity. It provides structured guidance on training, risk assessment, prevention, and respo
...
Response to the tropical cyclone in southern Africa
Ebola virus disease outbreak in the Democratic Republic of the Congo
Meningitis outbreak in Togo
Lassa fever
...
Following the declaration of the 9th Ebola Disease Outbreak (EVD) on 8 May 2018 by the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) Ministry of Health, the WHO has raised the alert for neighbouring countries of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) which
...
A toolkit for behavioural and social communication in outbreak response
This brief summarises key considerations about the social, political and economic context of Goma in relation to the outbreak of Ebola in the DRC as of March 2019. Goma is the administrative capital of North Kivu province and a major urban centre in
...
Not all that bleeds is Ebola
recommended
How has the DRC Ebola outbreak impacted Sexual and Reproductive Health in North-Kivu?
Recommendations (more specifics found in the assessment):
1. Sexual and reproductive health needs and services are to be embedded in the EVD response from the ou
...
This learning report attempts to understand the drivers for, and barriers to, effective implementation as well as review the experiences of Start Fund members in responding to these outbreaks to support evidence-based decision-making within the Start Network at project, crisis, and system level. Spe
...
ON LIFE SUPPORT3The Democratic Republic of Congo’s Ebola outbreak has been contained, but confl ict and under-development leave over three million children at risk from measles and other killer diseases. The country’s medical services – ill-eq
...
Learning from the Use of Data, Information, and Digital Technologies in the West Africa Ebola Outbreak Response
An 82 percent funding gap is putting the lives of 2.5 million people in north-west Syria at risk this winter.
The first cholera case in north-west Syria was confirmed on 19 September. See below for the latest updates.
On 17 September,
...
Summary of research into the consequences of the Ebola outbreak for children and communities in Liberia and Sierra Leone
This study describes the range of impacts that Ebola has had on children and families in Liberia and Sierra Leone, looking beyo
...
The official death toll has risen to 518 people as of 1 April, according to the Government.
• More than 1,000 cases of cholera and one death have been reported.
• Nearly 110,000 houses have been identified by the authorities as totally destroy
...