Filter
28781
Filtered Results: 204
Topics:
Children
Featured
Recommendations
2185
New Publications
6393
Language
Document type
No document type
13809
Studies & Reports
4130
Guidelines
3266
Fact sheets
1548
Manuals
1145
Resource Platforms
918
Infographics
850
Strategic & Response Plan
793
Training Material
608
Situation Updates
527
Videos
508
Brochures
298
Online Courses
270
Dashboards/Maps
82
App
29
Countries / Regions
Global
1470
India
991
Germany
920
Sierra Leone
521
Kenya
516
Congo, Democratic Republic of
501
Liberia
454
Latin America and the Carribbean
444
South Africa
444
Nepal
436
Nigeria
425
Russia
420
Ukraine
411
Ethiopia
406
Africa
389
Senegal
387
Western and Central Europe
377
Uganda
353
Syria
342
Myanmar / Burma
333
Indonesia
318
Brazil
316
Guinea
315
Rwanda
304
Burkina Faso
301
Bangladesh
294
Tanzania
289
Haiti
270
Venezuela
266
Mozambique
263
Malawi
259
Zambia
243
Yemen
221
Ghana
217
Eastern Europe
205
Paraguay
201
South Sudan
197
Colombia
195
West and Central Africa
190
Philippines
182
Middle East and North Africa
181
Namibia
178
Mali
168
Argentina
157
Benin
156
East and Southern Africa
150
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
144
Peru
139
Cameroon
137
Zimbabwe
130
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
125
Lesotho
115
Cambodia
113
South–East Asia Region
113
Asia
112
Angola
105
Central African Republic
104
Madagascar
103
Niger
94
Chile
90
Guinea-Bissau
84
Botswana
81
Bolivia
76
Chad
75
Lebanon
72
Somalia
71
Ecuador
71
Afghanistan
67
Pakistan
64
Eswatini/ Swaziland
61
Spain
54
Sudan
51
USA
49
China
48
El Salvador
46
Vietnam
45
Togo
41
Jordan
40
Iraq
40
Tajikistan
39
Thailand
37
Turkey
36
Western Pacific Region
35
Italy
33
North America
32
Mexico
30
Portugal
30
Switzerland
28
Canada
27
Moldova
27
Egypt
27
Sri Lanka
26
United Kingdom
25
Albania
24
Burundi
24
Singapore
23
Laos
23
Palestine
21
Kazakhstan
20
Iran
20
Honduras
20
Guatemala
20
Kyrgyzstan
18
Armenia
18
Saudi Arabia
18
France
18
Georgia
18
Greece
17
Libya
17
Malaysia
15
Papua New Guinea
14
North Macedonia
13
Dominican Republic
13
Belarus
13
Uzbekistan
12
Morocco
12
Southern Africa
12
Estonia
11
Congo-Brazzaville
11
Austria
11
Uruguay
11
Djibouti
11
Gambia
10
Ireland
10
Tunisia
10
Nicaragua
10
Romania
10
Poland
10
Timor Leste/ East Timor
9
Serbia
9
Hungary
9
Luxembourg
9
Algeria
9
Mauritania
8
Japan
8
Jamaica
7
Bhutan
7
Cuba
7
Turkmenistan
6
North Korea
5
Gabon
5
Belgium
5
South Korea
5
Azerbaijan
5
Australia
4
Fiji
4
Vanuatu
4
Mongolia
4
Croatia
4
Qatar
3
Cape Verde
3
Denmark
3
Mauritius
3
Israel
3
Bosnia and Herzegovina
3
Guyana
3
Bulgaria
2
Lithuania
2
Maldives
2
French Guyana
2
Latvia
2
Slovakia
2
Solomon Islands
2
Norway
1
Morocco
1
Slovenia
1
Barbados
1
Belize
1
Costa Rica
1
Eritrea
1
Oman
1
Panama
1
United Arab Emirates
1
Bahamas
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
COVID-19
2151
Studies & Reports
1647
Guidelines
1371
Statistics
1164
Policies
1093
Information, Education and Communication (IEC)
950
Women & Child Health
874
Policies & Guidelines HIV & TB
867
Humanitarian Crisis
795
Capacity Building
698
Community Health
603
Non-communicable Diseases
572
Demograhic Health Surveys DHS
526
Drugs & Medical Equipment
428
Disabilities
345
Humanitarian Aid
228
Maternal Health
218
Countries
217
Pediatrics
184
General Guidelines
179
Maternal & Child Health
172
Child Health
153
Disease Prevention & Control
144
Infection Control & Prevention (IPC)
138
Under-5 nutrition
137
Gynaecology & Obstetrics
134
WASH
131
Reproductive Health
129
Disaster Preparedness
124
Paediatrics
123
Surgery & Anaesthesia
122
Community Health
121
Neonatal Care
119
Food Security & Nutrition
119
Hand Hygiene
117
Mental Health
111
TB
111
Protection & Security
110
Online Courses & Platforms
109
HIV & STI
107
Other
102
Needs Assessment
91
Vaccine-preventable Diseases
88
Child protection
88
Sexual Violence
84
Age & Elderly
72
Water
71
Women & Child Health
69
Female Genital Mutilation
67
Family Planning
66
Primary Health Care
64
Key Resources
63
Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
62
Capacity Building
61
MPOX - Monkeypox
60
Immunization
60
Health Systems
59
Public Health
57
x MEDBOX Issue Brief & Annual Reports x
56
Water, Sanitation and Hygiene (WASH)
55
NCD
55
Sanitation
53
Cardiovascular Diseases
53
Palliative Care
52
Malaria
52
Clinical Guidelines
50
Public Health
48
Vector Control
48
Hygiene Promotion
48
Communicable Diseases
47
Clinical Training
46
Non-communicable Diseases NCD
45
Parasitology
45
General Guidelines
44
Cancer
43
Monitoring & Evaluation
43
Palliative Care
43
NTDs & Others
43
Hepatitis
42
Diabetes
42
IEC Material
39
Diarrhoeal Disease/Cholera
39
Global Health
39
Hemorrhagic Fever
37
Humanitarian Aid
36
Dental & Eye Care
34
Medical Devices & Equipment
34
Quality Control & Assurance
33
Waste Management
31
Nutrition
31
Health System Strengthening
30
Training Manuals
29
Diarrhoea
29
Virology
28
Leprosy
28
Pharmacy & Technologies
28
Bacteriology
27
Yellow Fever
27
Respiratory Infections
26
Mobile Training Tools & Apps
25
Violence against Children
24
Gender
22
Communicable Diseases
22
Fecal Disposal / Latrines
22
Dengue
22
Laboratory Quality Assurance
22
Emergency Health Kits
21
Dermatology
21
Neurology & Psychology
21
Cancer Treatment & Resources
20
Sex. & Repr. Rights
20
Leprosy
19
Cervical Cancer
18
Menstrual Hygiene Management
18
Yersinia pestis (Plague)
18
Leishmaniasis
18
Planetary Health
17
Pediatric cancer
17
Digital Health
16
Radiology and Diagnostic
16
Pharmacy & Technology
15
Rabies
14
Videos
14
Buruli Ulcer
13
Breast Cancer
13
Project Cycle Management
12
Hematology
12
Snakebites
12
COPD/Asthma
12
Laboratory Waste
11
Yaws
10
Maternal Health
10
COVID-19
10
Pharmaceutical Assessments
10
Chagas
10
Zika
9
Schistosomiasis
9
Palliative Care
9
Medicines Donations
7
Taeniasis/ Cysticercosis
7
Neurology & Psychology
7
xMEDBOX Videos
7
Helminthiasis
6
Online Courses Platforms
6
Community Health
6
Emergency Care
6
Disabilities & Inclusion
6
Trachoma
5
Lymphaticfilariasis
5
Annual Report MEDBOX
5
Laboratory Technologies
5
Disabilities
4
Mental Health
4
Pharmacy
3
Other Cancer diseases
3
General
3
Vaccine-preventable Diseases
3
HIV
3
Videos
3
Water & Sanitation
3
Onchocerciasis
2
Online Courses
2
Patient Care
2
Nutrition
2
Neglected Tropcial Diseases NTDs
2
TB
2
Laboratory
2
Human African Trypanosomiasis
2
Antimicrobial Resistance
1
Training material & manuals
1
Clinical Aspects & Management
1
Videos
1
Reproductive Health
1
Training material & manuals
1
Presentation & Lectures
1
E-therapy
1
Dracunculiasis
1
Toolboxes
Country specific documents
1555
For General Public & Community
392
Infection Control General
338
Children/Adolescents Mental Disorders
253
Poster & Infographics
227
Substance Use Disorders & Addiction
226
Clinical Guidelines
220
Social Worker
198
Health Financing Toolbox
184
For Parents & Children
178
IACAPAP International Association for Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Allied Professions
175
Assessment & Studies
168
For Health Worker
161
Global Impact: Socio-economic, health services, TB & HIV
144
Children & Adolescents
139
COVID-19 Information
138
Prevention & Preparedness
137
Diagnostics & Laboratory Guidance
137
Communication Material
131
Hand Hygiene
128
Neurological Disorders
126
Poster
126
Psychosocial Support (MHPSS)
124
Medical professionals
123
Hospital Readiness/Essential Health Services
121
Assessment & Response
121
PPE Personel Protective Equipment
120
Mental Health
119
Maps
118
Online Courses & Resources
116
Video & Audio
113
Surveillance & Contact tracing
109
General Information & Methodology
107
War & Conflict
106
Country specific
103
Detection & Diagnosis
103
Information & Education Material (IEC)
102
Context, Facts & Travel Advice
101
Climate Change General
101
Situation Reports & Updates
101
Roadmaps, Action Plans & Policies
101
For Migrants & Refugees
100
Community Health Workers CHW
100
MPOX - Monkeypox
100
Substance Use Disorders, Others
99
Psychosocial Support
95
Prevention & Control
94
Alcohol
92
Information & Education Material (IEC)
92
Public Health
90
Climate & Health
90
Mental Health
90
Videos
89
Children with Disabilities
85
Social Mobilisation
85
Vaccine Hesitancy & Myths
83
Pediatrics
83
Children & Mental Health
81
General Studies & Reports
80
Child Protection
79
Situation Reports & Updates
79
Child Protection
77
Drug resistant TB
77
Children & Mental Health
76
Education
76
Training
76
Surveillance
75
Planetary Health
75
Eastern Europe
74
Access & Strategy
74
Context & Facts, Travel Advice
73
Protection of Vulnerable Groups
73
Educational Settings
73
COVID-19 Vaccination Information
73
Training Material
73
Resource Platforms others
72
Adults
71
General Information
71
Human Rights
70
Coping with Stress
70
International
70
International
69
Clean air
69
Studies & Reports
69
Alzheimer's Disease & Dementia
69
Humanitarian Crisis
68
Policies
67
Health & Refugee
67
Assessment & Response
67
COVID-19
66
Information for the Public
66
Children
65
Health Impact & Climate Change
65
others
65
Training Supporting Material mhGAP
64
Human Rights
64
Studies & Reports
64
WASH
63
Manuals
63
Treatment Guidelines
63
Country-specific Platforms
63
MHPSS – Psychosocial Support
63
Handbooks & Manuals
63
IEC Materials
62
Essential Medicines & Medical Devices
62
Children's Rights
62
Nurses
61
Online Courses, Resources & Platforms
61
Self-harm & Suicide
61
Mythbusters/Misinformation
60
Immunization Guidelines
60
HIV testing & services
59
Policies & Programmes
59
Epilepsy
59
Infection Prevention & Hygiene
59
MPOX - Monkeypox
59
TB & Prisoners
59
Policy
59
Faith-based Organizations
58
Medical & Community Masks
58
Outbreak Prevention & Control
57
Scientific & Research Studies
57
Urban health
57
Women & Maternal Health
57
Guidelines & Manuals
57
General
57
Integration
56
Treatment & Prevention
56
Diagnosis & Treatment PTSD in Children
56
Midwives
56
PPE Personel Protective Equipment
55
Fair Allocation & Ethical Aspects
55
Humanitarian Crisis
55
Training Manuals
54
Communication & Training
54
Studies & Reports
54
Mental Health Guidelines
54
Appeals and Response Plans
54
Resource platforms
54
Information & Education Material (IEC)
54
General Reports
53
Violence & Protection
53
COVID-19 Vaccination
53
Rational use of Medicine
53
Disability Rights & Convention
52
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
52
Children with disabilities
51
Training, others
51
For Older People
51
Essential Medicines & Devices Lists
51
Posttraumatic stress disorder Adults
50
RCCE Guides & Manuals
50
Miscellaneous
50
Clinical Aspects, Treatment & Prevention
49
Key Resources
49
Context & Facts
49
MPOX -Monkeybox Prevention & Control
49
Protection
49
Assessment & Response
48
Inclusion
48
Discrimination & Stigma
48
Comics
48
Information, Resources & Websites
48
Global
47
Children
47
Paediatrics
47
Oxygen Therapy
47
Palliative Care
47
Studies & Reports
47
Anamnesis / Screening
46
Child Health / Pediatrics
46
Tips & Best Practice Examples
46
Mental Disorders
46
Capacity Building & Resources
46
Training Material
45
Gender Aspects
45
Long COVID/ Post-COVID Syndrome
45
General
45
Prevention & Strategies
45
Disease Prevention & Control
45
Inclusion in Humanitarian Settings
44
Europe
44
Germany
44
Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in Children
44
Studies
44
Dashboards & Maps
44
Guidelines
44
Waste Managment
44
IPC General
44
General Mental Health Guidelines
43
Germany
43
TB & Other Vulnerable Populations
43
Mental Health Studies & Reports
43
Sustainable Development Goals
43
Dashboards & Resource Platforms
43
Hand Hygiene
43
Health Promotion
43
Overview & reports
43
Pharmacy Practice
43
General documents One Health
43
Capacity Building & Resources
43
Roadmaps, Action Plans & Strategies
43
Postexposure Prophylaxis (PEP), Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
43
Situation Reports & Updates
43
Africa
42
Sexual and gender-based violence (SGBV)
42
Preparedness, Response & Risk Communication
42
WASH Water Sanitation & Hygiene
42
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
42
Information & Education Material (IEC)
42
Women
42
Agriculture & Veterinary
41
IPC
41
Infographics for Health Worker
41
Presentation
41
Zoonoses
41
Information & Education Material (IEC)
41
Prevention & Strategies
41
Assistive devices & technologies
41
Reproductive Health
41
Best Practice Models
40
Treatment Guidelines
40
IEC Substance Use Disorders
40
For Pregnant Women
40
Guiding documents and principles
40
Information Refugees Ukraine
40
Language Teaching
40
Situation Reports & Updates
40
Health Care Systems
40
Research
39
Others
39
Reports
39
For Community Health Workers
39
Inclusion
38
Human Rights, Stigma & Discrimination
38
Latin America
38
HIV and COVID-19
38
Advocacy & Communication
38
Poor Diet
38
Diseases Surveillance
38
Clinical Aspects
37
Training
37
Laboratory
37
Community Health
37
SARS-CoV-2 Variants
37
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
37
Capacity Building & Resources
37
Capacity Building & Resources
37
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
37
Studies & Reports
37
Situation Reports & Updates
37
Research & Access
37
Logistics & Supply
36
Studies & Reports
36
Prevention & Strategies
36
Disaster Preparedness & Prevention
36
Latin America & the Carribean
36
Laboratory & Sampling
35
Reports
35
Physical Distancing
35
Peru
35
Heat
35
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
35
Vector Control
35
Infographics
35
Resource Platforms
34
Background PTSD in children
34
Schizophrenia
34
Videos & Online Courses
34
Mental Health Online Resources
34
Hygiene
34
Online Courses
34
Disaster, Migration and Conflict
34
Epilepsy
34
Databases & Maps
34
Assessment & Response
34
Preparedness, Response & Risk Communication
33
Shelter & Reconstruction
33
El Niño
33
General
33
Food and Nutrition
33
Agriculture
33
Essential Medicines
33
Cerebral Palsy
33
General
33
Diarrhoea
33
Policies & Strategies
32
Dictionaries & Interpreting
32
Africa
32
HIV
32
e-Learning
32
Videos
32
Primary Care
32
Health Care Systems
32
Strategies & Roadmaps
32
Clinical Aspects & Diagnosis
32
Global Overview
32
Diagnostic & Laboratory
32
Diabetes
31
Others
31
Universal Health Coverage UHC and 90-90-90 Strategy
31
Health Personnel
31
Information & Education Material (IEC)
31
Studies & Reports
31
Online courses
31
Clinical Aspects & Diagnosis
31
Information & Education Material (IEC)
31
Emergency Prepardeness and Plans
31
CBM Inclusive Project Cycle Management Training
31
Gender Aspects
30
Drugs
30
Surveillance
30
Vaccination
30
mhGAP Guides
30
Ebola & Marburg
30
Standard Precautions
30
Toolkit on disability for Africa
30
Situation Reports & Updates
30
Statistics & Facts
30
Asia
30
Mental disorders, others
30
Gynaecology / Obstetrics
29
Curricula & Core Competencies
29
General
29
General
29
At Home
29
Tuberculosis
29
ART Drug Resistance
28
IEC Materials General
28
Hand Hygiene
28
IEC Material Mental Disorders
28
Stress
28
Risk Communication & Community Engagement
28
Prison & Detention
28
Colombia
28
Supply Chain & Store Management
28
Traditional & Herbal Medicines
28
Cancer
28
Studies & Reports
28
Hand Hygiene
28
Guidelines, Manuals & Toolkits
28
Asia and Pacific
28
IEC
28
Vision Loss & Blindness
28
Childhood TB
27
Vaccines & Immunization
27
Supporting tools
27
Waste Management
27
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
27
Resuscitation
27
Snakebite envenoming
27
Clinical Aspects & Diagnosis
27
Prevention & Strategies
27
Air Pollution
27
Asia
27
Natural Disaster
26
Local Action
26
Mental Health
26
Health Equity & Equality
26
Communication & Training
26
Cannabis
26
Long-term Care Facilities
26
Vaxzevria (Astra Zeneca)
26
Research & Pipeline
26
Internet Resources
26
Others
26
Information & Education Material (IEC)
26
Information & Education Material (IEC)
26
Studies & Reports
26
Malnutrition
26
Behaviour Change/Life Skill Education
25
Hygiene
25
Maps
25
Drugs / Medicines / Pharmacy
25
Camps and Camp-like Settings
25
Catholic Social Teaching (CST)
25
COVID-19
25
Stress
25
General Guidelines for Rational Use
25
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
25
Clinical Guidelines
25
Country specific Guidelines
25
Early Warning
25
War Surgery & Wound Care
25
Conflict
25
Hearing Loss & Deafness
25
Bipolar Affective Disorders
25
Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT)
25
Violence & Child Trafficking
24
Communication & Training
24
Faith-based Organizations
24
Clinical Guidelines
24
Opoids
24
Wheelchair Service and Management
24
Women's Mental Health
24
Key Resources
24
Infectious Diseases
24
Capacity Building & Resources
24
Studies & Reports
24
Studies & Reports
24
Autism
24
Male Circumcision
23
Video & Audio
23
Chemical Attacks
23
Measures ICF/ Model Disability Survey
23
Treatment Guidelines HIV
23
Biontech/Pfizer Comirnaty
23
Quality Assurance
23
Patient Safety
23
Health Worker
23
Context & Facts
23
Vaccination
23
One Health
23
Germany
23
Intellectual Disability
22
Ukraine
22
Platforms and initiatives
22
Advocacy
22
COVID-19
22
Risk Communication & Community Engagement
22
Workplace
22
COVID-19
22
Mental Health
22
Stigmatisation
22
Food environments
22
Falsified & Substandard
22
Pharmacovigilance
22
COVID-19
22
Global Impact of war
22
Studies & Reports
22
Capacity Building & Resources
22
Information & Education Material (IEC)
22
General
22
Resource Platform
22
Studies & Reports
21
Infection Control
21
Laboratory
21
Stigma & Discrimination
21
Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
21
Sitreps & Updates
21
Simulations
21
Encyclical Letters
21
Situation Reports COVID-19
21
Resources Kreyol Earthquake Haiti
21
Pharmacy Management
21
Agriculture incl. animal husbandry
21
Argentina
21
General
21
Education material
21
Psychosocial Support
21
Information & Education Material (IEC)
21
Vector control
21
Chemoprevention/preventive Treatment
21
Laboratory Guidance
21
Policies and guidelines
21
General Information Material
21
Global Mental Health
20
Prevention Guidelines
20
Interculturality
20
Hepatitis
20
People who injecting Drugs
20
Palliative Care
20
TB/COVID-19
20
Brazil
20
HIV &TB
20
Videos
20
Non-communicable Diseases NCD
20
Nuclear & Chemical Hazards
20
Health Care In Conflict Settings
20
Statistics & Facts
20
Overview, Studies & Reports
20
Key Population
20
Global Overview & Statistics
20
Education of students & professionals
20
Opportunistic Infections
19
HIV testing & disclosure
19
Legislative Texts
19
Sexual Abuse
19
For People with Disabilities
19
Health Care Professionals & Spirituality
19
Infection Control & Prevention (IPC)
19
TB/HIV
19
Biodiversity shift
19
Intensive Care Unit
19
Online courses
19
Environment
19
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
19
Humanitarian Aid Guidelines
19
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
19
Studies & Reports
19
Surveillance
19
TB & Drug Abuse
18
Accessibility
18
Introduction to Global Health
18
Context & Facts
18
Situation Reports & Updates
18
Sustainability
18
COVAX Initiative
18
Inactivated COVID-19 Vaccines
18
Others
18
Other Countries
18
Reports & Studies
18
Ethics
18
Statistics & Facts
18
Studies & Reports
18
Prevention & Strategies
18
Statistics & Facts
18
Capacity Building & Resources
18
Alcohol Consumption
18
Drug Abuse
18
Communication Strategies
18
Contact Tracing
18
Community Worker
18
Human Rights & the Right to Health
18
TB/HIV Global
18
Prevention
18
HIV support organizations
17
People with Handicaps
17
Statistics & Data
17
Pediatrics
17
Information for Refugees & Migrants
17
Stroke
17
For Health Professionals
17
Travel Advice
17
Livestock production
17
Clinical Guidelines
17
Country Specific
17
LGBTI*
17
Others
17
El Salvador
17
Advocacy
17
Videos
17
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
17
Echinocccosis
17
Earthquake in Türkiye and the Syrian Arab Republic
17
Advice for travellers
17
Risk Communication & Community Engagement (RCCE)
17
Clinical Guidelines
17
Technical Information
17
Moldova
16
Communication & Training
16
For General Public
16
Diverse Chemical Substances
16
Sexually Transmitted Infections
16
Vaccination
16
Covid-19 & the One Health Approach
16
Principles of Solidarity
16
Ebola Treatment Center
16
Ethics
16
Strategies
16
Ukraine
16
Prevention & Measures
16
Resource Platforms
16
Capacity Building & Resource platforms
16
Onchocerciasis
16
Yaws & other Endemic Treponematoses
16
Prevention & Control
16
Statistics & Facts
16
Co-Morbidities (except TB)
16
Stewardship
16
Clinical Guidelines
15
HIV in Children:Mental Health & Psychosoc. support
15
Cancer
15
Vector Control
15
Surgery & Rehabilitation
15
Physiotherapy & Rehabilitation
15
Concepts of Global Health
15
Men who have sex with men (MSM)
15
Syria
15
Microcephaly
15
Information for different audiences
15
Manual & Leaflet
15
Social Ethics
15
Statistics & Facts
15
Studies & Reports
15
Studies & Reports
15
Foodborn trematodiasis
15
Access to treatment and laboratory
15
Official Development Assistance
15
Prevention & Control
15
Drug Resistance
15
IEC Material Children
15
IEC Materials Children
15
Public Health
14
Early Warning
14
Refugee
14
Transgender People
14
Genomic sequencing
14
mRna Vaccines general
14
Vector-based Vacines General
14
Medical Records/Documentation
14
Green & healthy living
14
Surgery
14
Capacity Building & Resources
14
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
14
Statistics & Facts
14
NTDs General
14
Capacity Building & Resources
14
Online Courses & Webinars
14
Video & Audios
14
General Aspects
14
Online Courses
13
HIV surveillance
13
Latin America
13
Videos
13
Cholera
13
Russia
13
Option for the Poor
13
Blood Supply
13
Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs)
13
Environmental NPIs
13
Moderna
13
Online Resources
13
Booster Doses
13
Food & Nutrition
13
Others
13
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
13
Information & Education Material (IEC)
13
Romania
13
National Emergency Response Plans
13
Translation & Language Teaching
13
IEC Material/BSCC
13
Biosafety
12
Training
12
Dental Health
12
For Project Management
12
South Sudan
12
Orphans & vulnerable children
12
Surveillance
12
Cholera
12
Clinical Guidelines
12
Essential List
12
Child Friendly Spaces (CFS)
12
COVID-19 Simulation Exercise Training
12
Latin America
12
Chile
12
Mobility
12
Freshwater use
12
Climate Change
12
Resource Platforms
12
Disability Prevention & Rehabilitation
12
Studies & Reports
12
Prevention & Control
12
Capacity Building & Resources
12
Environmental Factors
12
Community Based Rebabilitation (CBR)
12
Malawi
12
Nutrition
12
Prevention of Disabilites
12
Laboratory Guidance
11
International
11
Rwanda
11
Technical Information
11
HIV / AIDS
11
Psychosocial Support
11
Sex Worker
11
Topics
11
Clinical Aspects
11
Sanitation
11
Extreme Situations
11
Others
11
Guidelines General
11
Situation Reports& Updates
11
Pharmaceutical Assessments
11
Land-system change
11
Mental Health
11
Water Pollution
11
Resource Websites One Health
11
Best Practice Examples
11
Appeals & Response Plans
11
Capacity Building & Resources
11
Statistics & Facts
11
Policies & Strategies
11
Soil-transmitted helminthiasis
11
Clinical Aspects & Diagnostics
11
Tobacco Consumption
11
Essential Medecines & Medical Devices
11
International Health Regulations (IHR)
11
Early Warning Systems
11
Modules
11
Context & Facts
11
Technical Information
11
Early Warning
10
Maps
10
Hepatitis
10
Drug resistance
10
TB
10
IEC Materials
10
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
10
Training
10
Yemen
10
Key Resources
10
Information Material &Training
10
Public Health
10
Common Good
10
Pastoral Care
10
Structural Violence
10
Mindfulness
10
Triage
10
More Clinical Guidelines on Palliative Care
10
Planetary Boundaries Overview
10
Pakistan Flood 2022
10
Capacity Building & Resources
10
Statistics & Facts
10
Prevention & Control
10
Dracunculiasis (guinea-worm disease)
10
Leptospirosis
10
Scabies
10
Statistics & Facts
10
Physical Condition
10
Clinical Guidelines Women & Children
10
International Guidelines and Protocols
10
Policies & Strategies
10
Prophylactic Treatment
10
Uganda
10
Demographic Transition
9
Policies & Strategies
9
Explosives
9
Natural Disasters
9
South Africa
9
Namibia
9
Tools for Rational use
9
Adherence
9
Preparedness, Response & Risk Communication
9
Mozambique
9
Vaccination & Strategy
9
Overview
9
Spirituality
9
Public Health
9
Education Principles
9
Emergency health kits
9
Statistics & Facts
9
Mycetoma, Chromoblastomycosis & other deep mycosis
9
Awareness
9
Domestic Resource Mobilization
9
Capacity Building & Resources
9
Malaria and co-infection
9
Control & Eradication
9
Community Engagement
9
Case Studies & Lessons Learned
9
Ghana
9
Regions
9
Urbanization
9
Clinical Guidelines
9
Cocaine
8
Azerbaijan
8
Training
8
Asthma & COPD
8
Assessment & Response
8
SOPs
8
Georgia
8
Priority Assistive Products
8
Country Guidelines
8
Volunteer Engagement
8
Vaccine Candidates & Research
8
Johnson & Johnson
8
Self-care
8
Pocket Cards
8
Ecuador
8
Prices and Patents
8
Emergency health kits
8
More Information Refugee and Health
8
Waste management
8
Information & Education Material (IEC)
8
Information & Education Material (IEC)
8
Community Based Rehabilitation (CBR)
8
Others
8
Epidemiology
8
Life Cycle
8
Health Systems
7
Intercultural Competence
7
Physical Disability
7
Eastern Mediterranean Region
7
Public Health
7
Training Manuals
7
Online Resources
7
Prevention & Control
7
International
7
Drug resistance
7
Clinical aspects
7
GO pre-deployment training
7
Ethiopia
7
Human Dignity
7
General Background
7
Gambling
7
Capacity Building
7
Wound management
7
Planetary Boundaries
7
Medicine Donations
7
Biogeochemical flows
7
Online Courses
7
Capacity Building & Resources
7
Statistics & Facts
7
Statistics & Facts
7
Armenia
7
Communication & Social Mobilisation
6
Advocacy
6
National Policies
6
Key Resources
6
South Sudan
6
Communication
6
Risk Communication
6
COVID-19
6
Subsidiarity
6
Children
6
Covaxin
6
Estonia
6
Information & Education Material (IEC)
6
Taeniasis/Cysticercosis
6
Clinical Aspects & Diagnosis
6
Apps
6
Risk Assessment & Reduction
6
National and Regional Policies
6
General
6
Technical Information
6
Guillain-Barré Syndrome
5
WPRO (Western Pacific Region)
5
Neuropsychology of Trauma
5
Humanitarian Settings
5
Disability
5
African Region
5
Laboratory
5
Public Health
5
European Resource
5
Covid-19 & Climate Change
5
Humanitarian Aid
5
WASH Resource Platforms
5
Model Formulary
5
Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms
5
Various Target Groups
5
Economics
5
COVID-19
5
Leishmaniasis
5
Capacity Building & Resources
5
Factsheets
5
Other NTDs
5
Risk Factors
5
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
5
Public Health
5
Go-pre deployment Training
5
Social Behaviour Change and Communication
5
IEC
5
Global Health Education
5
AR (African Region)
5
Clinical Guidelines
4
Eating Disorders
4
Prophylaxis
4
Workplace
4
Belarus
4
Mental Health & Psychosocial Support
4
Advice for Different Audiences
4
Patient care
4
One Health
4
Information & Education Material (IEC)
4
Online Courses
4
General Information & Methodology
4
Socio-Economic & Demographic
4
Prevention & Control
4
Key Resources
4
Outbreak Response
4
Emergency Medical Team (EMT)
4
Clinical Guidelines
3
Clinical Guidelines
3
Zambia
3
Capacitiy Building
3
Training
3
Key Resources
3
Sputnik V
3
Caregiver
3
Standard precautions
3
Latin America
3
Clinical Guidelines
3
Capacity Building & Resources
3
Studies & Reports
3
Gynaecological Cancers
3
Data Collection and Analysis
3
Rapid Response Team (RRT)
3
Botswana
3
Bioterrorism
3
Clinical Guidelines
3
Albania
3
Lesotho
3
Understanding Global Health
3
Rapid Response
2
Clinical Guidelines
2
High Risk Groups
2
Natural Hazards
2
Strategies & Action Plans
2
Key Resources
2
DR Congo
2
Best Practice
2
Resource Platforms
2
Covid-19 TOOLBOX
2
African Region
2
Key resources
2
Pharmacy
2
Health Consequences
2
Social Ethics in Health Work
2
Dengue & Chikungunya
2
Geographical Distribution & Statistics
2
West and central Africa
2
NCDs
2
Clinical Aspects & Diagnosis
2
Detection and Surveillance
2
Reporting Mechanism
2
Liberia
2
Regional Reports & Guidelines, others
2
Africa
2
Disability (CBR)
2
Key Resources
1
Statistics & Facts
1
Public Health
1
Key Resources
1
Types of Disability
1
Research & Development
1
Workshop Preparation Material
1
Poster
1
Guiding documents
1
Capacity Building
1
NTDs
1
Buruli Ulcer
1
Rabies
1
Lymphatic filariasis
1
Videos
1
Tungiasis
1
Cardiovascular Diseases
1
Diabetes
1
Chronic Respiratory Diseases
1
Key Resources
1
Clinical Aspects
1
Response
1
Mental Health & Psychosocial Support
1
Technology & Innovation
1
Others
1
HIV and Sexual Reproductive Health
1
Discrimination & Stigma
1
Children & Adolescents
1
Prevention
1
HIV resilience interventions
1
Women
1
Polio
1
Key Resources
1
Sierra Leone
1
Senegal
1
Coronavirus disease 2019 has a mild disease course in children and adolescents. Chronic respiratory conditions, including asthma, have been suggested as risk factors; however, asthma in children is highly variable in both triggers and severity.
During the pandemic, pediatric asthma services limite...
Key facts
- A healthy diet helps to protect against malnutrition in all its forms, as well as noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including diabetes, heart disease, stroke and cancer.
- Unhealthy diet and lack of physical activity are leading global risks to health.
- Healthy dietary practices start...
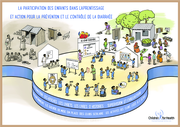
Le document fournit des messages éducatifs et des conseils pratiques pour prévenir et gérer la diarrhée, en particulier chez les enfants. Il met l'accent sur les pratiques d'hygiène telles que le lavage des mains adéquat, l'utilisation de latrines et la manipulation sûre des aliments. Il soul...
Asthma is the commonest chronic childhood disease and encompasses a spectrum of airway diseases with similar symptoms. Inaccurate diagnosis remains common, especially in younger children, with failure to characterize the different “asthmas.” Children worldwide repeatedly suffer symptoms which se...
Как детям живется после страшных переживаний и как можно им помочь. Собрание картин, составленное Сузаннэ Штайн (Susanne Stein) для разговоров с родителями детей, пережив...
Як живеться дітям після пережитого надзвичайно великого страху і що їм може допомогти. Брошура Сюзанне Штайн (Susanne Stein) для розмов з батьками дітей, які пережили над�...
Little is known about asthma control in the rising number of African children who suffer from this condition. The Achieving Control of Asthma in Children in Africa (ACACIA) study is an observational study collecting evidence about paediatric asthma in urban areas of Ghana, Malawi, Nigeria, South Afr...
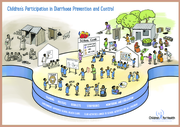
The document provides educational messages and practical guidance to prevent and manage diarrhoea, particularly in children. It emphasizes hygiene practices like proper handwashing, using latrines, and safe food handling. It also highlights the importance of breastfeeding, balanced nutrition, immuni...
Our aim is to review current asthma epidemiology, achievements from the last 10 years, and persistent challenges of asthma man- agement and control in low-middle income countries (LMICs). Despite global efforts, asthma continues to be an important public health problem worldwide, particularly in poo...
Under-diagnosis of asthma in ‘under-fives’ may be alleviated by improved inquiry into disease history. We assessed a questionnaire-based screening tool for asthma among 614 ‘under-fives’ with severe respiratory illness in Uganda. The questionnaire responses were compared to post hoc consensu...
Lancet Glob Health 2020 Published Online October 22, 2020 https://doi.org/10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30325-9
The Zambia Malaria Campaign, implemented by Breakthrough ACTION, used culturally tailored radio adverts and a campaign song to encourage key behaviours for preventing and treating malaria. The campaign targeted high-risk groups, such as pregnant women and caregivers of children under five, and deliv...
Pregnant travelers face numerous risks, notably increased susceptibility to or severity of multiple infections, including malaria. Because pregnant women residing in areas non-endemic for malaria are unlikely to have protective immunity, travel to endemic areas poses risk of severe illness and pregn...
Every two minutes, a child under the age of 5 dies from malaria. Under-five children accounted for 67 per cent of all malaria deaths worldwide in 2018. Most of them occurred in sub-Saharan Africa where an estimated 24 million children were infected with its deadliest form. In addition to being the t...
The document focuses on educating children and communities about diarrhoea prevention and management through creative and interactive approaches. It highlights the importance of hygiene practices, oral rehydration solutions (ORS), zinc supplements, and proper nutrition to combat diarrhoea. Developed...
Asthma is one of the neglected diseases in Africa with a high prevalence. Allergic fungal diseases have been reported to complicate asthma progression and treatment outcomes. However, data about fungal asthma and its associated complications are limited in Africa. We aimed to estimate the burden of ...
Risk factors for asthma among schoolchildren who participated in a casecontrol study in urban Uganda
Data on asthma aetiology in Africa are scarce. We investigated the risk factors for asthma among schoolchildren (5–17 years) in urban Uganda. We conducted a case-control study, among 555 cases and 1115 controls. Asthma was diagnosed by study clinicians. The main risk factors for asthma were tertia...
The global prevalence, morbidity and mortality related to childhood asthma among children has increased significantly over the last 40 years. Although asthma is recognized as the most common chronic disease in children, issues of underdiagnosis and undertreatment persist. There are substantial globa...
The article "Asthma treatment in children: A guide to screening for and management of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression" discusses the risks associated with the use of corticosteroids in pediatric asthma treatment. It highlights that prolonged corticosteroid use can suppress the hypoth...