Filter
8891
Filtered Results: 8891
Text search:
deaths
Featured
Recommendations
695
New Publications
2384
Language
Document type
No document type
4876
Studies & Reports
1611
Guidelines
914
Manuals
390
Strategic & Response Plan
322
Fact sheets
310
Training Material
143
Situation Updates
136
Infographics
78
Resource Platforms
66
Brochures
23
Dashboards/Maps
9
Online Courses
7
Videos
6
Countries / Regions
Global
421
India
396
Kenya
242
Sierra Leone
226
Liberia
195
Ethiopia
194
Nigeria
178
Nepal
173
Uganda
161
South Africa
158
Western and Central Europe
140
Rwanda
135
Myanmar / Burma
133
Bangladesh
129
Africa
126
Latin America and the Carribbean
125
Zambia
124
Tanzania
123
Malawi
121
Syria
107
Ghana
103
Congo, Democratic Republic of
92
Philippines
84
Namibia
82
Ukraine
81
Mozambique
75
Brazil
70
Zimbabwe
68
South Sudan
68
Asia
64
South–East Asia Region
64
Yemen
62
Senegal
59
Haiti
59
Cambodia
59
Lesotho
58
Guinea
58
Indonesia
56
West and Central Africa
51
Eastern Europe
50
Venezuela
47
Russia
46
Middle East and North Africa
44
East and Southern Africa
44
Botswana
36
Burkina Faso
34
Eastern Europe and Central Asia
32
Germany
31
Cameroon
27
Afghanistan
25
Eswatini/ Swaziland
24
Central African Republic
23
Somalia
23
Madagascar
22
Colombia
21
Sudan
21
Pakistan
20
Mali
19
Thailand
17
USA
16
Western Pacific Region
16
Lebanon
16
Tajikistan
14
Albania
14
Peru
14
Paraguay
14
Angola
14
Benin
13
Iraq
13
Jordan
12
North America
12
Vietnam
11
Moldova
11
Sri Lanka
11
Turkey
10
China
10
Chile
9
Guinea-Bissau
9
Côte d’Ivoire / Ivory Coast
9
Argentina
9
Papua New Guinea
9
Palestine
9
Georgia
9
Ecuador
9
Laos
8
Chad
8
North Macedonia
7
Mexico
7
Togo
7
Kyrgyzstan
7
Niger
7
United Kingdom
7
Southern Africa
7
Bolivia
7
Egypt
7
Libya
7
Iran
6
Burundi
6
Armenia
6
Greece
6
Timor Leste/ East Timor
5
Gambia
5
Kazakhstan
5
Uzbekistan
5
Jamaica
5
Canada
4
Italy
4
Hungary
4
Saudi Arabia
4
Portugal
4
El Salvador
3
Serbia
3
Morocco
3
Turkmenistan
3
Mauritius
3
Tunisia
3
Spain
3
Djibouti
3
Poland
3
Honduras
3
Bhutan
3
North Korea
2
Fiji
2
Estonia
2
Qatar
2
Mauritania
2
Ireland
2
French Guyana
2
Bosnia and Herzegovina
2
Romania
2
Switzerland
1
Mongolia
1
Bulgaria
1
Dominican Republic
1
Lithuania
1
Gabon
1
Japan
1
Denmark
1
Belgium
1
France
1
Norway
1
Azerbaijan
1
Belarus
1
Israel
1
Oman
1
Nicaragua
1
Slovakia
1
Guatemala
1
Authors & Publishers
Publication Years
Category
Countries
3549
Clinical Guidelines
668
Public Health
479
Women & Child Health
443
Key Resources
410
Capacity Building
165
Pharmacy & Technologies
45
Annual Report MEDBOX
3
Toolboxes
COVID-19
820
HIV
632
Mental Health
613
TB
464
Ebola & Marburg
347
Planetary Health
321
NCDs
288
Rapid Response
241
Conflict
241
Caregiver
231
NTDs
216
AMR
187
Refugee
163
Global Health Education
158
Disability
149
Natural Hazards
135
Malaria
119
Cholera
98
Health Financing Toolbox
96
Pharmacy
80
Social Ethics
58
Specific Hazards
55
Zika
40
2.0 Rapid Response
37
Polio
32
Typhoon
5
South Sudan
1
Excessive consumption of salt (more than 5 g per day) raises blood pressure, a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke, and is the leading cause of death in the WHO European Region. Many countries in the Region have initiated national salt reduction strategies,...
The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2010 projects that noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) will be responsible for over 44 million deaths during the next decade, representing an increase of about 15% since 2010. Most of these deaths will occur in the WHO ...
Policy Guidance Brief 2
• The potential health risks from climate change include: increase of waterborne and vector-borne diseases, heat-related illnesses, injuries and deaths, food insecurity and increased malnutrition. The poor, women, children and the elderly, as well as communities living...
• The potential health risks from climate change include: increase of waterborne and vector-borne diseases, heat-related illnesses, injuries and deaths, food insecurity and increased malnutrition. The poor, women, children and the elderly, as well as communities living...
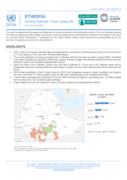
The Ethiopia Cholera Outbreak - Flash Update #8 reports a worsening cholera crisis, with 11,407 cases and 156 deaths as of June 20, 2023. The outbreak, ongoing since August 2022, has spread across 79 districts in Oromia, Somali, SNNP, and Sidama regions, increasing by 85% since May.
Key challenges ...
The Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste has the highest TB incidence rate in the South East Asian Region - 498 per 100,000, which is the seventh highest in the world. In Timor-Leste TB is the eighth most common cause of death.
The salient observations are as follows:
In 2018, 487 (12.5%) of the...
The "Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases 2013-2020," published by the World Health Organization (WHO), provides a roadmap to reduce premature deaths from noncommunicable diseases (NCDs) like heart disease, cancer, and diabetes. It emphasizes strengthening he...
This booklet presents data on NCD mortality and prevalence of NCD risk factors, by country, for the Region of the Americas. The focus is on the 5 x 5 NCD agenda which includes the main NCDs (cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes, and chronic respiratory diseases), and mental health (suicide); as...
This report highlights the increasing public health
burden of road traffic injuries and fatalities in
the Region. Road traffic deaths are becoming a
significant problem in Africa, rising at a faster rate
than in any other region. Fatalities increased by
nearly one fifth in the decade from 2010 ...
Antimicrobial resistance represents a big threat to public health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimate that every year two million Americans are infected with a (multi-)drug resistant bacterium, resulting in 23,000 deaths. The WHO has repeatedly drawn attention to this majo...
The world is not on track to end the AIDS pandemic. New infections are rising and AIDS deaths are continuing in too many communities. This report reveals why: inequalities are holding us back. In frank terms, the report calls the world’s attention to the painful reality that dangerous inequalities...
Nepal is on target to meet the Millennium Development Goals for maternal and child health despite high levels of poverty, poor infrastructure, difficult terrain and recent conflict. Each year, nearly 35000 Nepali children die before their fifth birthday, with almost two-thirds of these deaths occurr...
Policy brief, 24 July 2020
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected older people disproportionately, especially those living in long-term care facilities. In many countries, evidence shows that more than 40% of COVID-19 related deaths have been linked to long-term care facilities, with figures being as h...
By almost any measure, human health is better now than at any time in history. Life expectancy has soared from 47 years in 1950–1955, to 69 years in 2005–2010, and death rates in children younger than 5 years of age have decreased substantially, from 214 per thousand live births in 1950–1955, ...
These new guidelines should help medical and paramedical professionals to provide the state of art rabies prophylaxis to all animal bite victims in the government hospitals and prevent human rabies deaths in the state. The medical officers whenever in doubt are encouraged to contact the state nodal ...
Background: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases (ASCVD) including myocardial infarction, stroke and peripheral arterial disease continue to be major causes of premature death, disability and healthcare expenditure globally. Preventing the accumulation of cholesterol-containing atherogenic lipopr...
Diabetes mellitus (hereafter referred to as diabetes) is a chronic, progressive disease characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. Diabetes can lead to complications such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and premature death, and can damage eyes, kidneys and nerves. Globally, more than 400 millio...
WEEKLY EPIDEMIOLOGICAL RECORD, NO 23, 7 JUNE 2024, pp.307-318
The most recent estimate of the global number of deaths from dog-mediatedrabies is 59 000 per year.1 Rabies is associated with a 99.9% fatality rate and severe trauma in families in which a rabies death
occurs, and remains a major publ...
The United Nations Commission on Life-Saving Commodities (UNCLSC, 2012) defined 13 health products to end preventable deaths of woman and children. One of those 13 products is the neonatal resuscitator, is indispensable medical device to save newborns from asphyxia at birth. For the efficient use of...
It is estimated that more than 311 000 women die of cervical
cancer each year. Of these deaths, 91% occur in low- and
middle-income countries. Demographic changes and a lack of
action mean that the number of deaths per year is projected
to reach 460 000 by 2040.
Swahili version of Prevention and Management of Primary Postpartum Haemorrhage-PPH. Translation and voice over thanks to Alex Mureithi and Zawadi Machibya and their colleagues at the BBC Swahili Service.
PPH, or excessive bleeding after delivery, accounts for a third of all maternal deaths in sub-S...